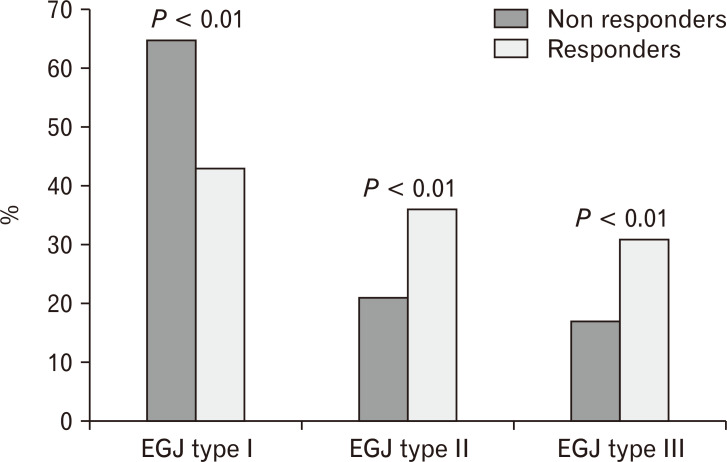
Figure.
Proportion of responders and non-responders in patients with Type I, II, and III esophagogastric junction (EGJ). There were statistically more non-responders among patients with Type 1 EGJ. In contrast, with EGJ disruption, the likelihood of response was statistically higher, indirectly indicating that the presence of EGJ disruption was a marker for abnormal reflux burden.