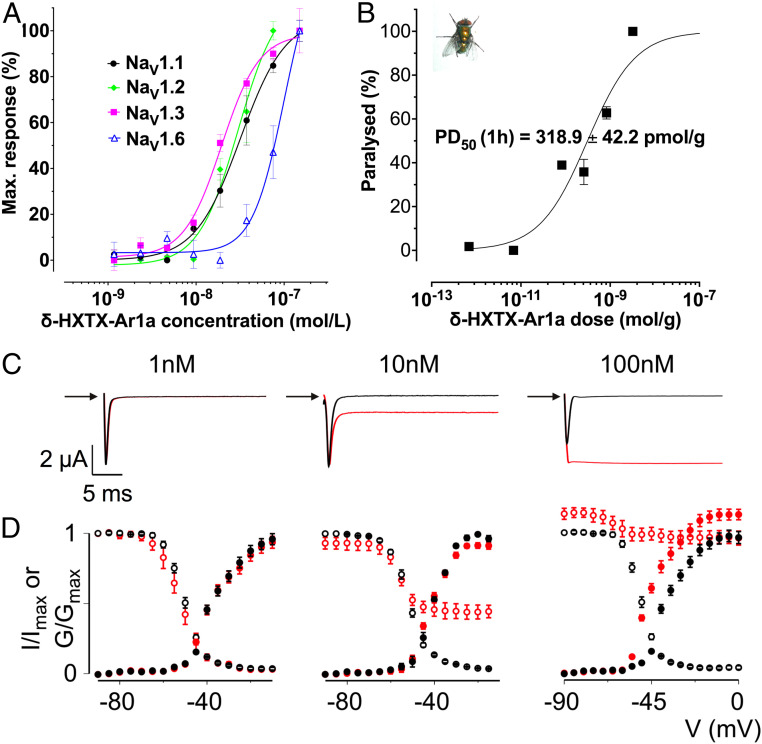
Fig. 5.
Biological characterization of Ar1a. (A) NaV subtype selectivity of Ar1a. The effect of Ar1a on NaV1.1 to NaV1.8 heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells in combination with the human b1 subunit was assessed using a membrane potential assay. Ar1a elicited a concentration-dependent increase in membrane potential in the presence of veratridine (5 µM) in cells expressing NaV1.1 (pEC50 7.52 ± 0.24), NaV1.2 (pEC50 7.41 ± 0.09), NaV1.3 (pEC50 7.41 ± 0.15), and NaV1.6 (pEC50 7.04 ± 0.08). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). (B) Dose–response curve for paralysis of L. cuprina blowflies (shown in Inset) injected with Ar1a. Paralysis was assessed at 1 h postinjection. Error bars indicate SEM. The PD50 was determined as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. All paralytic effects were reversible within 24 h and no lethal effects were observed. (C) Dose-dependent inhibition of BgNaV1 fast inactivation by Ar1a. Representative sodium currents were elicited by a depolarization to −20 mV before (black) and after (red) addition of toxin from a holding potential of −90 mV. (D) Normalized conductance–voltage relationships (G/Gmax; black filled circles) and steady-state inactivation relationships (I/Imax; black open circles) of BgNaV1 before (black circles) and after (red circles) Ar1a application. Channel-expressing oocytes were depolarized in 5-mV steps from a holding potential of −90 mV. Error bars represent SEM; n = 3 to 5.