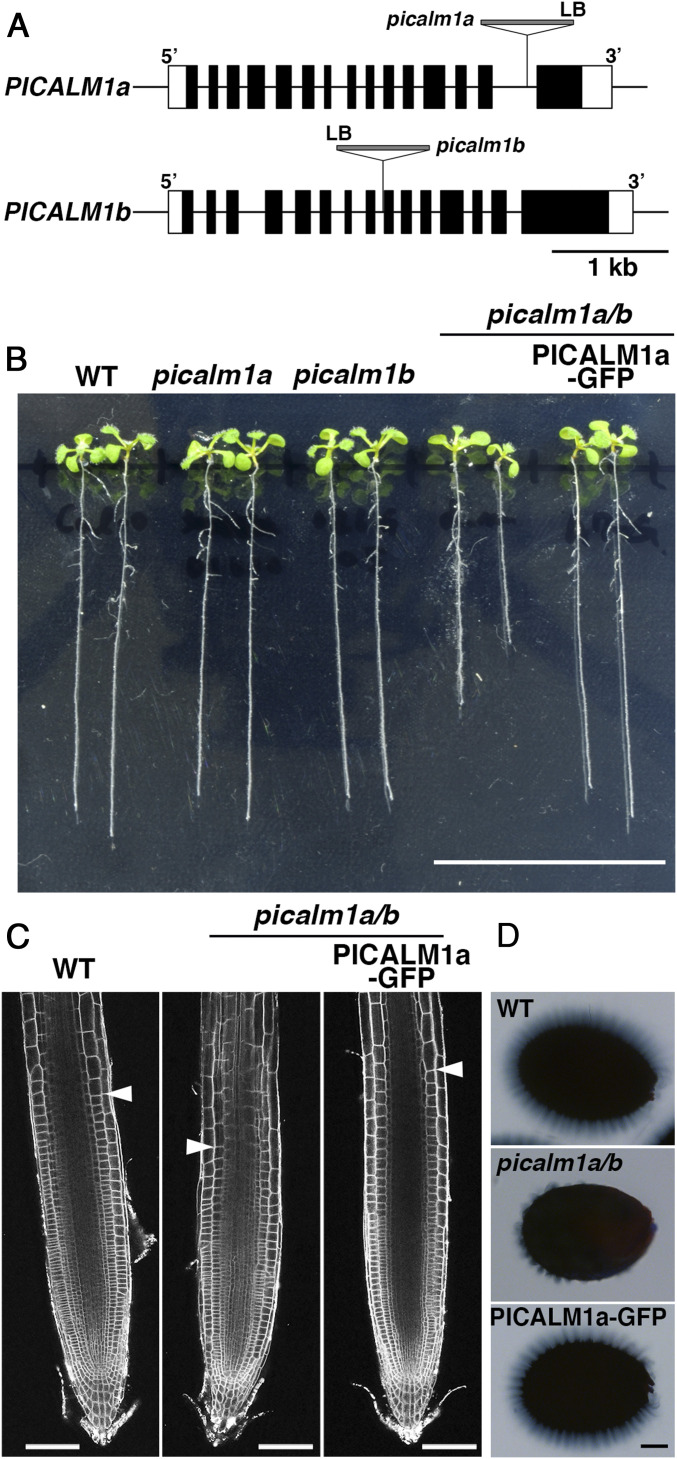
Fig. 3.
Effects of picalm1 mutations on plant development. (A) Schematic presentation of gene models for PICALM1a and PICALM1b and T-DNA insertion sites in picalm1a and picalm1b mutants used in this study. (B) Ten-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings of wild-type (WT), picalm1a, and picalm1b single mutants, picalm1a picalm1b (picalm1a/b) double mutant, and the double mutant transformed with PICALM1a-GFP. (C) Confocal images of root meristematic zones of the WT, picalm1a picalm1b double mutant (picalm1a/b), and double mutant transformed with PICALM1a-GFP and stained with FM4-64. The arrowheads indicate the boundary between the meristematic and elongation zones. (D) Seed coat mucilage after the imbibition of the WT, picalm1a picalm1b double mutant (picalm1a/b), and double mutant transformed with PICALM1a-GFP (PICALM1a-GFP) stained with ruthenium red. (Scale bars: 3 cm in B; 100 μm in C and D.)