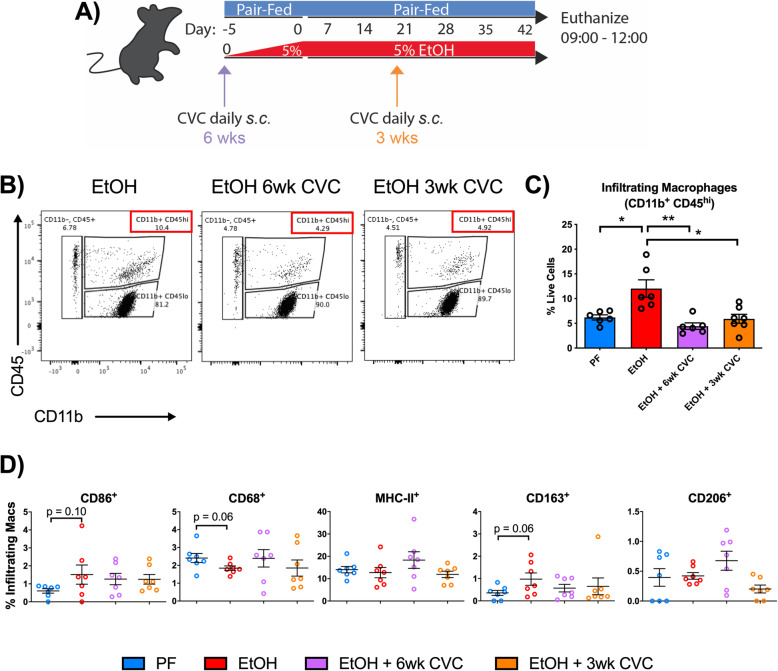
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of CCR2/5 signaling reduces CNS macrophage infiltration without altering activation marker expression of infiltrating macrophages. a Mice received a pair-fed diet (PF) or chronic alcohol (EtOH), and some alcohol-fed mice received 6 weeks of daily preventive subcutaneous CVC injection (EtOH + 6wk CVC) or 3 weeks of daily CVC treatment (EtOH + 3wk CVC). PF and EtOH mice received daily vehicle control injections. b Representative flow cytometry plots of peripheral macrophages (CD11b+ CD45hi) in EtOH, EtOH + 6wk CVC and EtOH + 3wk CVC-treated mice. c Quantification of infiltrating brain macrophages (CD11b+ CD45hi) in pair-fed, alcohol-fed, and treatment groups. d Expression of various activation markers were measured by flow cytometry in CD11b+ CD45hi infiltrating macrophages including CD86, CD68, MHC-II, CD163, and CD206. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 6–7 mice/group. *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA