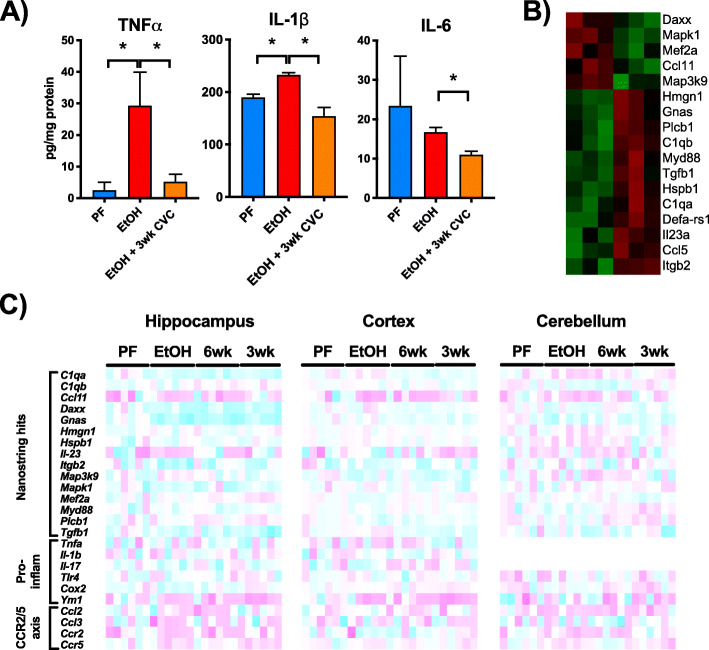
Fig. 4.
Chronic alcohol induces inflammatory gene expression changes in multiple brain regions. a Proinflammatory cytokine proteins TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 were measured from the hippocampus of pair- (PF) and alcohol-fed (EtOH) as well as alcohol-fed mice treated with CVC for 3 weeks (EtOH +3wk CVC) by ELISA. b Inflammatory gene expression of pair- and alcohol-fed mice was analyzed using the Nanostring nCounter Immunology Panel and revealed 17 genes significantly altered in the cerebellum (green, expression increased; red, expression decreased). c Gene expression changes of genes found by Nanostring to be altered as well as some common inflammatory markers, and CCR2/5 axis genes were measured in the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum by qPCR in a larger cohort of pair- and alcohol-fed mice as well as mice treated with 3 or 6 weeks CVC (purple, > 3-fold increase in expression; cyan > 3-fold decrease in the expression compared to PF; complete gene expression profile data found in Tables 3, 4, and 5). Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4–6 mice/group. *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA