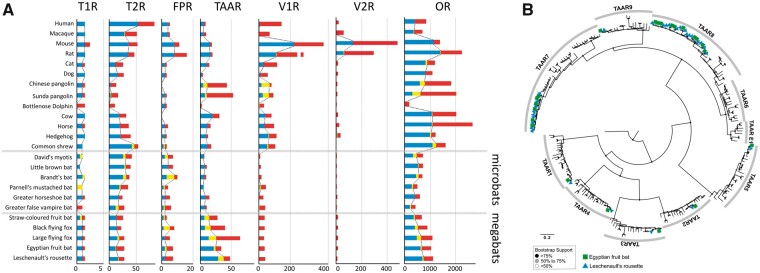
Figure 3.
Comparison of the copy numbers of seven chemosensory receptor genes for 24 mammals. (A) The number of intact, truncated, and pseudo-genes is indicated in blue, yellow, and red, respectively. We treated the truncated genes as ‘putatively intact’. The dotted lines show the variation in the number of intact + ‘putatively intact’ genes among mammals. It should be noted that the number of TAARs is obviously higher in megabats than in microbats. (B) Phylogenetic tree of intact TAARs in 24 mammals. Only the intact genes were included in the tree. The TAARs of the Egyptian fruit bat and Leschenault’s rousette are indicated by the square (green) and triangle (blue). It is obvious that the TAARs of subfamilies seven and eight were expanded in two Rousettus bats. Zebrafish TAAR13c in the NCBI database was used as an outgroup. Mouse TAAR1-9 in the NCBI database was used as an indicator for each TAAR subfamily. Accession codes for these database-derived genes are available in Supplementary Fig. S4.