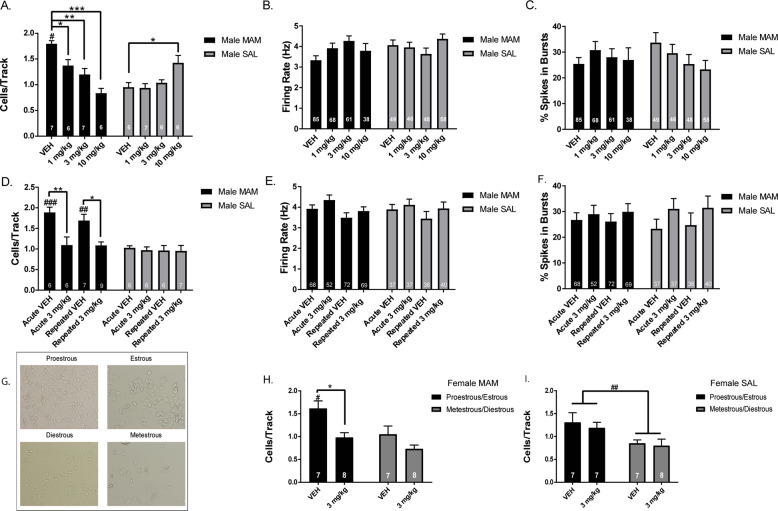
Fig. 1. Pomaglumetad dose-dependently reduces DA neuron population activity in MAM rats.
a In all, 30 min following POM i.p., MAM rats displayed a dose-dependent reduction in the number of spontaneously active DA neurons in the VTA compared to MAM rats that received VEH, which was not observed in SAL rats. There were no significant differences in the firing rate (b) or percentage of spikes in bursts (c) between POM and VEH administration in MAM or SAL rats. d There was no tolerance in the reduction in DA neuron population activity following 14d repeated POM treatment in MAM rats, compared to acute treatment. There were no significant differences in the firing rate (e) or percentage of spikes in bursts (f) following either acute or repeated treatment in MAM or SAL rats. g Example pictures of proestrous (high density of nucleated cells and cornified cells), estrous (high density of cornified cells with leukocytes), metestrous (low density of cell debris, few cornified cells) and diestrous (low density of leukocytes and nucleated cells) (h) MAM rats displayed higher DA neuron population activity in proestrous/estrous compared to diestrous/metestrous. In all, 30 min following POM i.p., MAM rats in proestrous/estrous displayed a reduction in DA neuron population activity (i). SAL rats displayed higher DA neuron population activity in proestrous/estrous compared to diestrous/metestrous with no significant effect of POM administration. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 within groups #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 between groups.