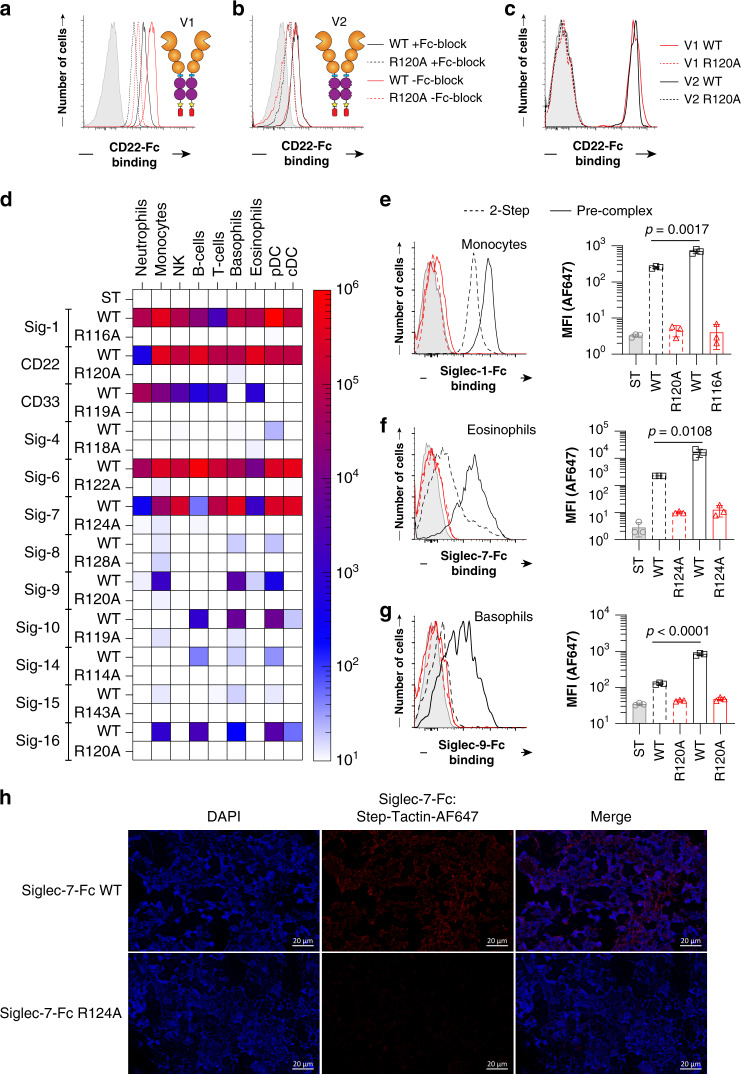
Fig. 3. Profiling Siglec ligands on primary human immune cells.
a Binding of CD22-Fc V1 WT (red) and R120A mutant (black) to neutrophils that were pretreated with Fc receptor block (dashed) or without (solid) followed by staining with Strep-Tactin-AF647. Control staining (gray) is Strep-Tactin-AF647 alone. b Binding of CD22-Fc V2 WT (red) and R120A mutant (black) to neutrophils that were pretreated with Fc receptor block (dashed) or without (solid). c CD22-Fc V1 (red) or V2 (black) binding to B-cells. d Flow cytometry data of Siglec-Fc constructs that bound after pre-complexing with Strep-Tactin-AF647 to B-cells (CD19+), T-cells (CD3+), NK cells (CD56+), monocytes (CD14+), neutrophils (CD15+), eosinophils (Siglec-8+), basophils (CCR3+), pDCs (CD123high/HLA-DR+), and cDCs (CD123dim/HLA-DR+). e–g Binding to the indicated WT (black) and arginine mutant (red) Siglec-Fc to e monocytes, f eosinophils, and g basophils in either a 2-step assay (dashed) or pre-complexed assay (solid). h Immunofluorescence staining of human spleen with Siglec-7-Fc WT or Siglec-7-Fc R124A. Immunofluorescent staining was repeated three times with similar results. Error bars represent ± standard deviation of three replicates. Statistical significance calculated based on a two-tailed unpaired Student’s T-test.