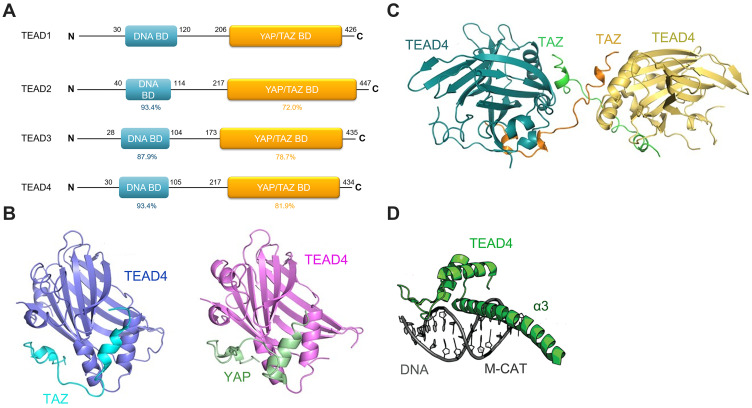
Figure 1.
(A) The overall structure of TEADs. TEADs consist of a TEA DNA binding domain (blue) and a YAP/TAZ binding domain (yellow). The percent represents the identity for each domain of TEADs compared to that of TEAD1. (B) YAP binds to TEAD4 via two short helixes and an extended loop containing the PXXΦP motif. TAZ interacts with TEAD4 in a similar manner to the binding of TEAD4-YAP. (C) Two TAZ molecules straddle two TEAD molecules to form a heterotetramer. (D) The α3 helix of the TEA domain (green) binds to the M-CAT DNA duplex (grey).
Notes: Images Figure 1B and C are adapted from Kristal Kaan HY, Chan SW, Tan SKJet al Crystal structure of TAZ-TEAD complex reveals a distinct interaction mode from that of YAP-TEAD complex. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–11. 10.1038/s41598-017-02219-9. Creative Commons license and disclaimer available from: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode.21Figure 1D reproduced from Holden JK, Cunningham CN. Targeting the hippo pathway and cancer through the TEAD family of transcription factors. Cancers (Basel). 2018;10 (3). 10.3390/cancers10030081. Creative Commons license and disclaimer available from: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode.20