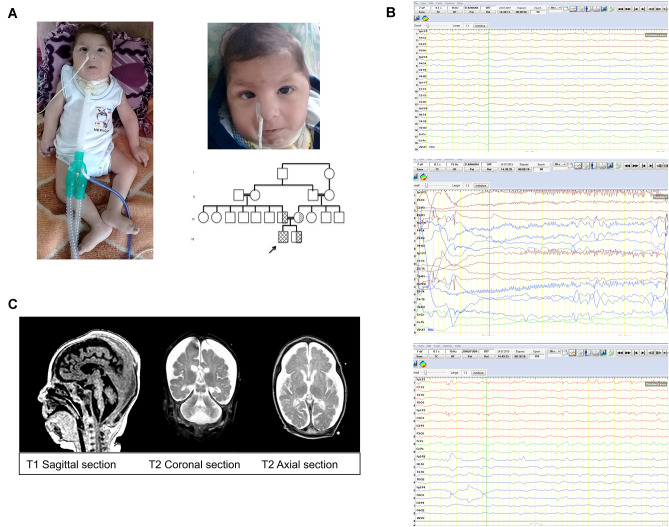
Fig. 1.
Clinical photographs, pedigree, EEG, and cranial MRI of the patient. A Dysmorphic features of the affected patient; note bitemporal narrowing, periorbital puffiness, down-slanted palpebral fissures, sparse eyebrows, round facies, broad nasal bridge, bulbous nasal tip, prominent philtrum, thin lips, and micrognathia, pedigree of the patient. B EEGs of the patient: (a) ground rhythm consists of slow and disorganized amplitude theta rhythm, superposed, low-amplitude fast activity according to age. (b) during this period, a low-amplitude fast beta activity, which started from the left hemisphere frontal region and reflected on the left hemisphere electrodes, was observed for 5–6 s, followed by an asymmetric tonic ictal seizure record with right-hand rotation, and then a few beat clones in the right arm. (c) in the Fp1–Fp3 electrode position, low-amplitude thorn slow waves at a frequency of 1–2 Hz were observed in interictal activity. C Brain magnetic resonance imaging demonstrating atrophic corpus callosum, cortical laminas necrosis in both occipital and superior parietal lobes, simple spiral pattern in cortical structures, hypomyelination and brainstem, and cerebellar vermis hypoplasia compatible with pontocerebellar hypoplasia