Figure 3.
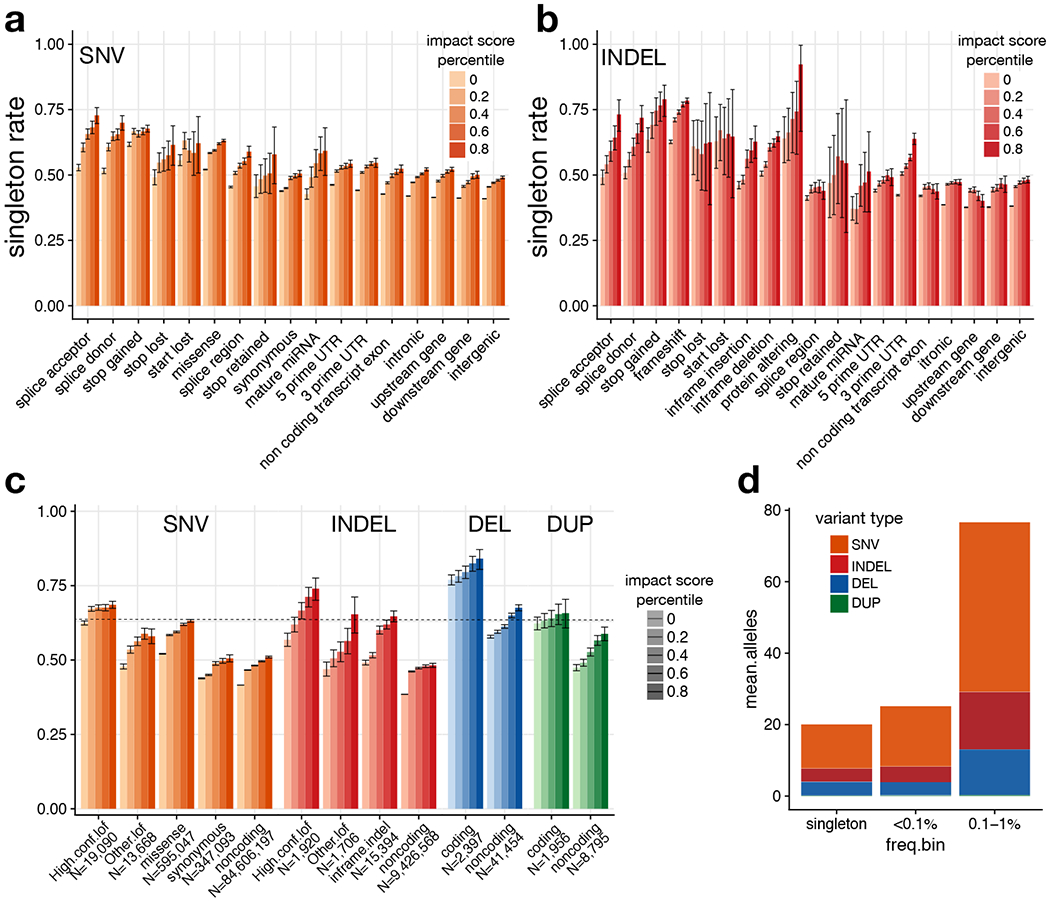
Estimation of genome-wide burden of high-impact functional alleles. (a) Singleton rates for SNV, by VEP consequence and percentile of combined VEP/CADD impact score. (b) Singleton rates for indels. (c) Singleton rates by variant type and percentile of combined VEP/CADD impact score. Here, “other LoF” indicates VEP-annotated protein-truncating variants (PTVs) that are not classified as high-confidence by LOFTEE. DELs and DUPs that intersect any coding exon of the principal transcript are classified as “coding”; otherwise they are “noncoding”. The horizontal line shows the singleton rate for all high confidence SNV/indel LoFs. (d) Per-sample mean number of “strongly deleterious” alleles genome-wide, by type and frequency class. In panels (a)-(c), error bars indicate the 95% confidence interval (Wilson score method). See Supplementary Table 6 for counts of variants in each category.
