Fig. 1.
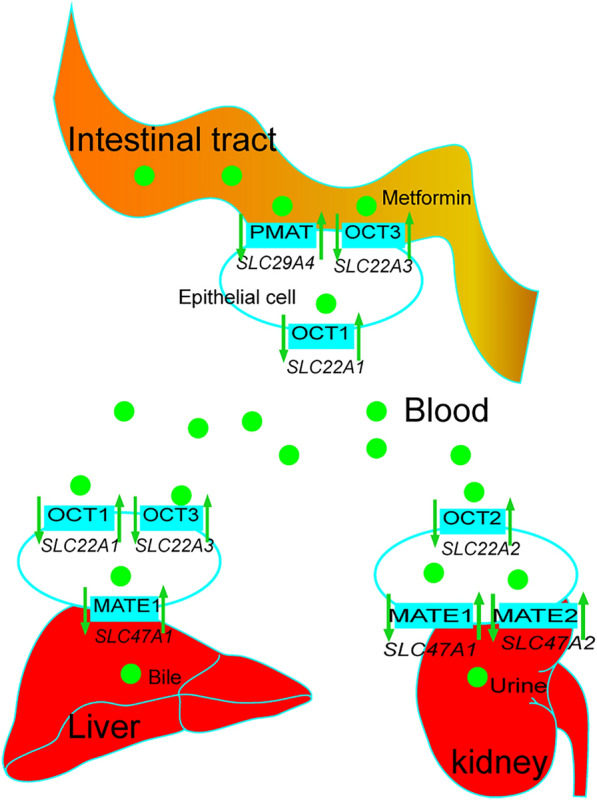
The pharmacokinetic process of metformin and the potential effect of its pharmacogenomic genes. After entering the gastrointestinal tract, metformin in intestinal endothelium is absorbed into intestinal epithelial cells by PMAT (encoded by SLC29A4) and OCT3 (encoded by SLC22A3), and transported into blood by OCT1 (encoded by SLC22A1). When metformin gets to the liver, OCT1 and OCT3 in membranes of hepatocytes take it up, and MATE1 (encoded by SLC47A1) transports it into the liver where it is ultimately eliminated with bile. Metformin also is taken up into epithelial cells of the kidney by OCT2 (encoded by SLC22A2). MATE1 and MATE2 (encoded by SLC47A2) are responsible for excretion of metformin into urine
