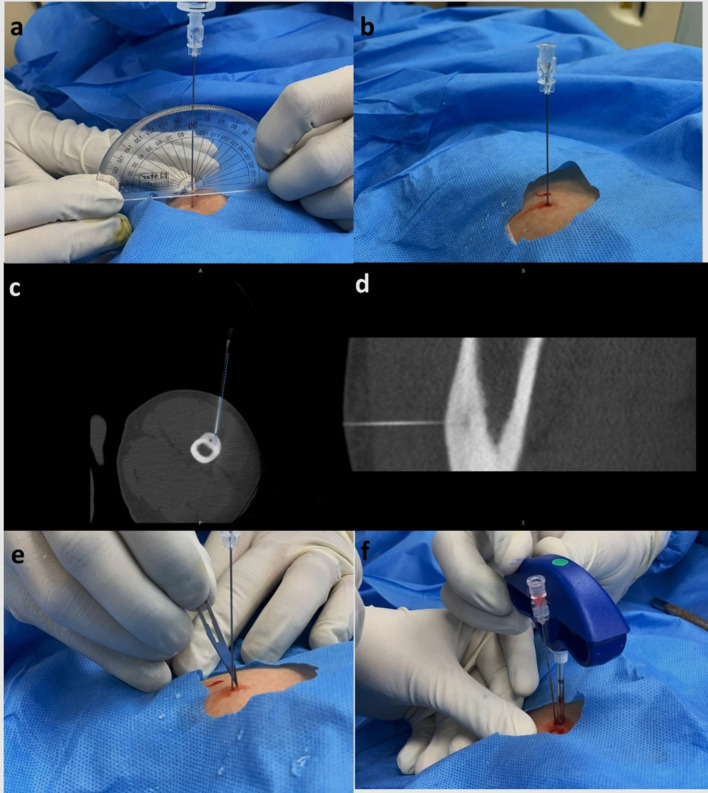
Figure 6.
(a–f) Concept of rail-road technique. After marking the length on the spinal needle, (a) the needle is inserted at 90° to the lesion using a protractor, while simultaneously infiltrating local anaesthesia along the tissue planes till the bone is reached. (b) Once the needle is advanced till the bone, a scan is acquired to ascertain needle position. (c,d) Axial and sagittal CT image showing the spinal needle reaching up to the cortex overlying the nidus. Observe that the needle trajectory (dotted blue line) is slightly lateral to the location of the nidus. Keeping this in mind, (e) a small incision is made medial to the spinal needle and (f) the introducer needle is advanced along the spinal needle till the cortex. The spinal needle is subsequently removed.