Figure 6.
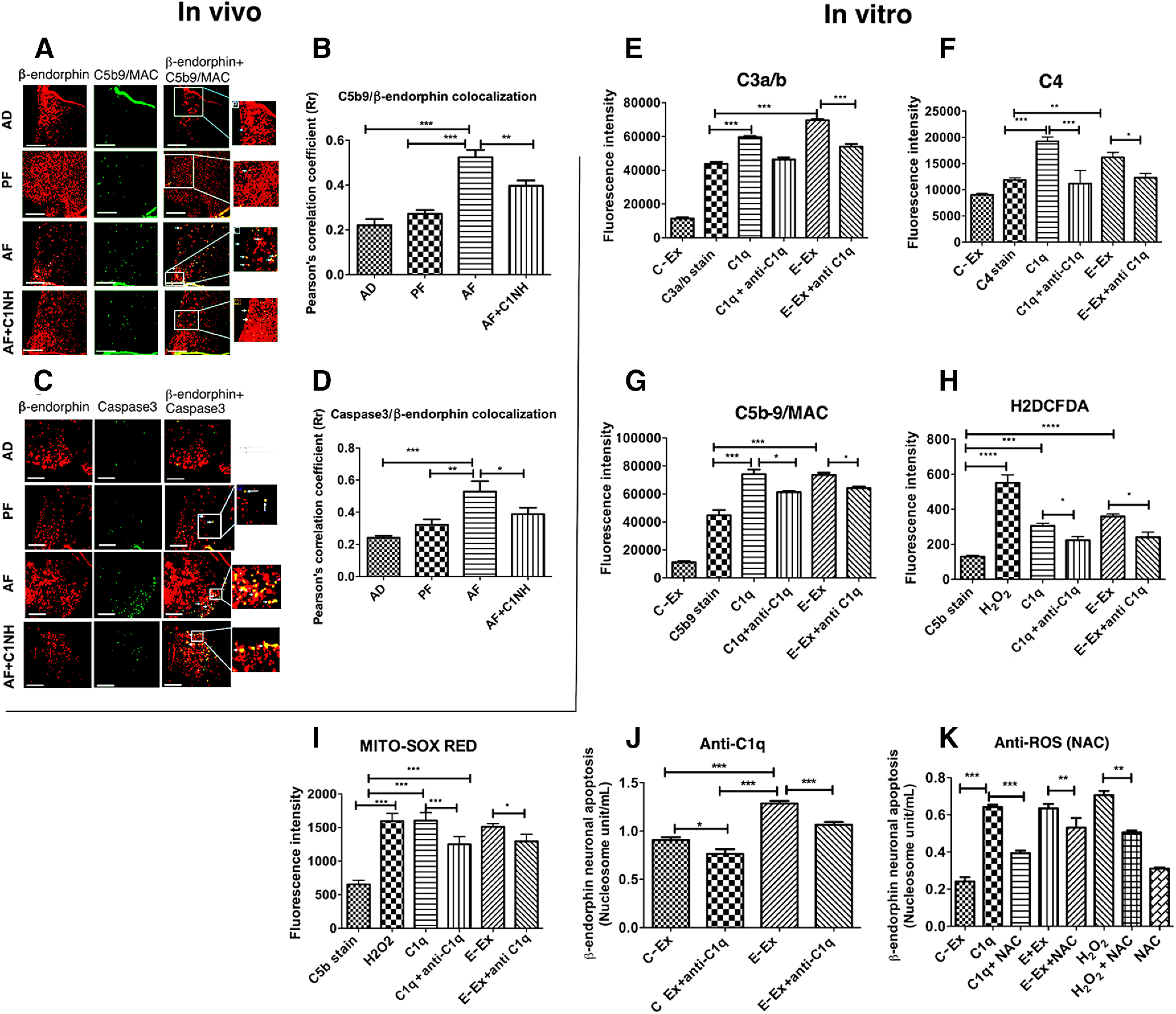
Role of the C1q-activated complement pathway in ethanol-induced cell death of β-endorphin neurons in the hypothalamus. A, B, Representative images of β-endorphin-positive staining (red) and C5b9-positive staining (green), along with merged images and zoomed pictures to demonstrate colocalization (A). Scale bars, 50 μm. Histograms represent the mean ± SEM values of Pearson's correlation of C5b9 colocalization with β-endorphin (B) in AD-, PF-, AF-, and AD+C1NH (100 U/kg)-treated rat pups on PND 6 (n = 7-9). C, D, Representative images of β-endorphin-positive staining (red) and caspase 3-positive staining (green), along with merged images and zoomed pictures to demonstrate colocalization (C). Scale bars, 50 μm. Bar graphs representing mean ± SEM values of Pearson's correlation of caspase 3 colocalization with β-endorphin (D) in AD-, PF-, AF-, and AD+C1NH-treated rat pups on PND6 (n = 7). E–G, Flowcytometric analysis of C3a/b (E), C4 (F), and C5b-9 expression (G) on β-endorphin neurons in primary cultures treated with ethanol-activated (50 mm) microglial exosomes or recombinant C1q protein (500 ng) with or without anti-C1q (C1q neutralizing antibody; 1:25 dilution) for 2 h. H, I, Flowcytometric analysis of cellular ROS by H2DCFDA (H) or mitochondrial ROS by MITO-SOX RED (I) on β-endorphin neurons treated with H2O2 (40 μm) for 30 min, ethanol-activated (50 mm) microglial exosomes, or recombinant C1q protein (500 ng) with or without anti-C1q (C1q neutralizing antibody; 1:25 dilution) for 2 h. J, K, Effects of anti-C1q (C1q neutralizing antibody; 1;25 dilution; J) or anti-ROS NAC (10 μm; K) in control-treated microglial exosomes (C-Ex) or ethanol-treated (50 mm) microglial exosomes (E-Ex)-induced changes in β-endorphin neuronal apoptosis as determined by nucleosome assay in primary cultures of β-endorphin neuronal cells. Data are mean ± SEM (N = 4-6). *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, ***p< 0.001.
