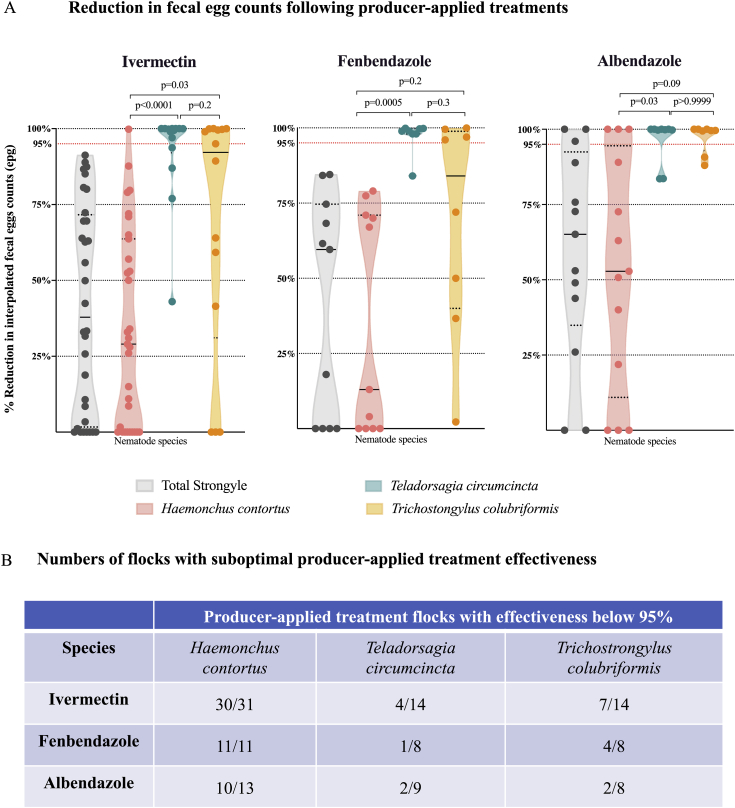
Figure 2.
Use of ITS-2 rDNA nemabiome metabarcoding to determine effectiveness of producer-applied anthelmintic treatments against specific gastrointestinal nematode species in western Canada.
Panel A. Reductions in fecal egg counts following producer-applied treatments interpolated from ITS-2 rDNA nemabiome data for specific gastrointestinal nematode species.
Relative species abundance, determined by ITS-2 rDNA nemabiome metabarcoding in each sample pre- and post-treatment, was used to interpolate species-specific eggs counts and treatment effectiveness for each group in 56 producer-applied treatment samples. Violin plots show drug effectiveness based on the reduction of total strongyle-type fecal egg counts (grey) and the effectiveness against Haemonchus contortus (pink), Teladorsagia circumcincta (teal) and Trichostrongylus colubriformis (orange) for ivermectin, fenbendazole and albendazole, respectively. Dotted lines represent quartiles and solid lines represent median of each violin plot. Statistical significance of the differences between the groups was determined by Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test using GraphPad Prism version 8.1.0 for macOS, GraphPad Software, San Diego, California USA, www.graphpad.com.
Panel B. Numbers of flocks with suboptimal producer-applied treatment effectiveness . Each cell in the table shows the number of flocks with specific treatment effectiveness below 95%/total number of flocks tested with ivermectin, fenbendazole and albendazole against Haemonchus contortus, Teladorsagia circumcincta and Trichostrongylus colubriformis respectively.