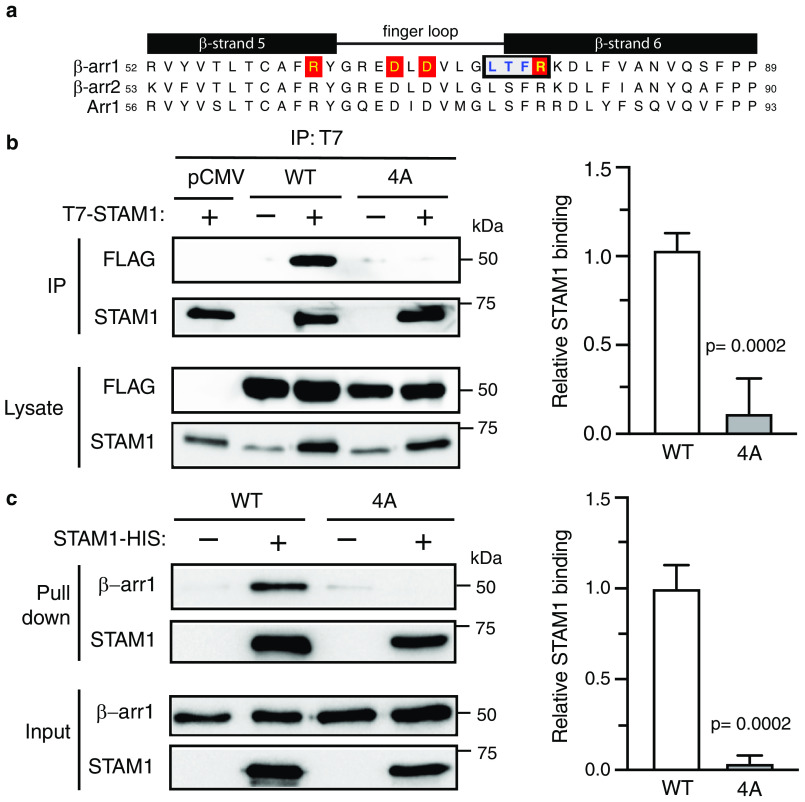
Figure 6.
Biochemical analysis of β-arr1 WT and finger-loop mutant (4A) binding to STAM1. a, sequence alignment of β-strand 5, finger loop, and β-strand 6 of bovine β-arr1 (residues 52–89), β-arr2 (residues 53–90), and visual arrestin (Arr1, residues 56–93). Boxed residues denote the four residues that were substituted to alanine residues in β-arr1. Letters highlighted in red denote residues that are identified to form two ionic locks to maintain the finger loop in an inactive bent conformation. b, cleared lysates from HEK293 cells co-transfected with T7–STAM1 and β-arr1–WT–FLAG, β-arr1–4A-FLAG, or empty vector (pCMV) were incubated with an anti-T7 antibody. Immunoprecipitates (IP) were analyzed by immunoblotting to detect bound β-arr1. Shown are representative immunoblots. Bound STAM1 was quantified by densitometric analysis. The graph represents the fraction of STAM1 bound to β-arr1–WT–FLAG from three independent experiments. The error bars represent the S.D. The data were analyzed by an unpaired t test. The p values are indicated. c, equimolar amounts of purified β-arr1–WT or β-arr1–4A (0.4 μm) were incubated with or without purified STAM1–HIS (3 μm) for 20 min at 37 °C. Complexes were captured by incubation with Talon cobalt resin, and after washing, the proteins were eluted in binding buffer supplemented with 200 mM imidazole and analyzed by immunoblotting. Representative blots are shown. Bound STAM1 was quantified by densitometric analysis. The graph represents the fraction of STAM1 bound to β-arr1 from three independent experiments. The error bars represent the S.D. The data were analyzed by an unpaired t test. The p values are indicated.