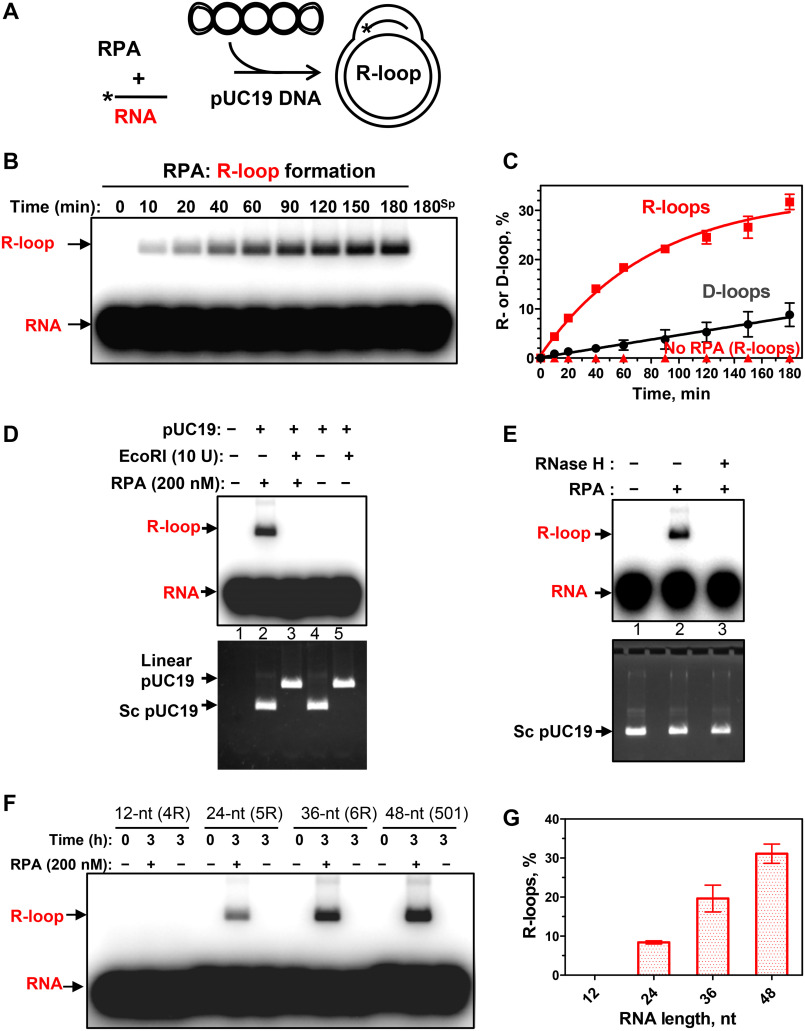
Figure 2.
RPA promotes R-loop formation. A, reaction scheme. *, 32P label. B, kinetics of the R-loop formation by RPA (200 nm) analyzed by electrophoresis in a 1% agarose gel. 180sp, reaction (180 min) in the absence of RPA. The stoichiometric ratio of RNA/dsDNA was 5:1 (in molecules). C, graphical representation of R- and D-loop formation by RPA. D, sensitivity of R-loops to EcoRI cleavage. 32P-labeled RNA (no. 501; 3 μm, nt) was incubated with supercoiled pUC19 dsDNA (67.2 μm, nt) for 3 h in the presence of RPA (200 nm, lanes 2 and 3) or in its absence (lanes 4 and 5). The R-loops were then incubated with EcoRI (lane 3). The products were analyzed by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gel. Controls include [32P]RNA (no. 501; 3 μm, nt) (lane 1) and a mixture of 32P-labeled RNA (no. 501; 3 μm, nt) and pUC19 incubated with EcoRI storage buffer (lane 4) or with EcoRI (lane 5). The gel was autoradiographed (top) to visualize 32P-labeled RNA and R-loops and then stained with ethidium bromide (bottom) to monitor intactness of supercoiled pUC19 dsDNA and its cleavage by EcoRI. Note that R-loops co-migrate in the gel with supercoiled pUC19 DNA. E, sensitivity of R-loops to RNase H. The R-loops produced as in D (lane 2) were incubated with RNase H (5 units) (lane 3) or with the storage buffer (lane 2). The products were analyzed as in D. F, RNA length dependence of R-loop formation by RPA. R-loops were formed by RPA (200 nm) in pUC19 DNA (67.2 μm, nt) using 32P-labeled RNAs: 12-mer (no. 4R), 24-mer (no. 5R), 36-mer (no. 6R), and 48-mer (no. 501) (each 3 μm, nt). R-loops were analyzed by electrophoresis in a 1% agarose gel. G, data from F presented as a graph. Error bars, S.E.