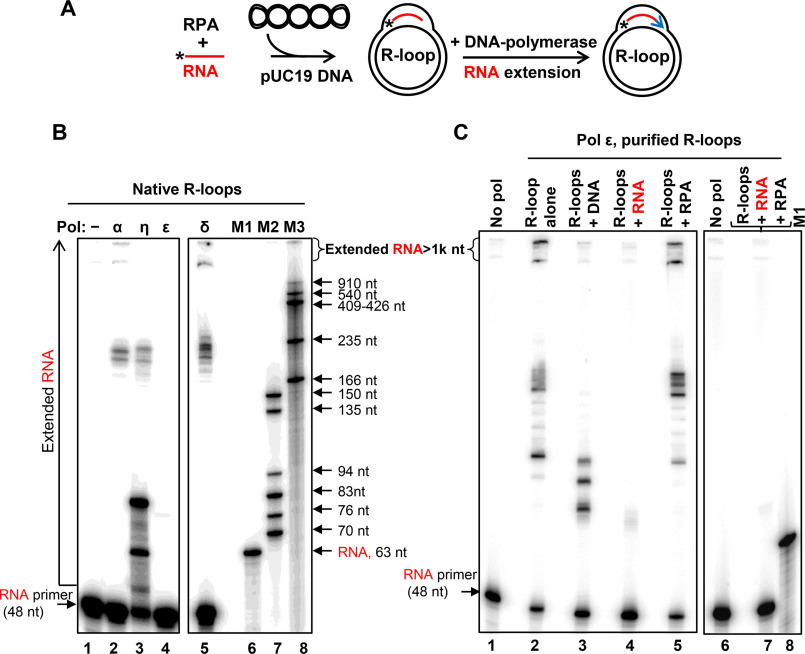
Figure 5.
In vitro reconstitution of DNA synthesis restart from R-loops. A, experimental scheme. *, 32P label at 5′-end of RNA (48 nt of no. 501). Blue arrow, extension of RNA by DNA polymerases. B, R-loops (3 nm) were generated in pUC19 using RPA. RNA extension in R-loops was carried out using DNA pol α (50 nm), η (38 nm), ε (50 nm), or pol δ (0.5 nm). The products of RNA extension were analyzed by electrophoresis in 8% polyacrylamide denaturing gels. In control (lane 1), DNA polymerases were omitted. 32P-labeled markers are shown in lanes 6–8. C, effect of RNA, ssDNA, RPA, and RPA-RNA on DNA synthesis by pol ε. RNA extension by pol ε (50 nm) was carried out using deproteinized and purified R-loops (1 nm) (lane 2). The R-loops were premixed with ssDNA (no. 2; 3 μm, nt) (lane 3), RNA (no. 517; 3 μm, nt) (lane 4), RPA (5 nm) (lane 5), or a mixture of RPA (200 nm) and RNA (no. 517; 3 μm, nt) (lane 7) prior to pol ε addition. In control (lanes 1 and 6), pol ε was substituted with storage buffer.