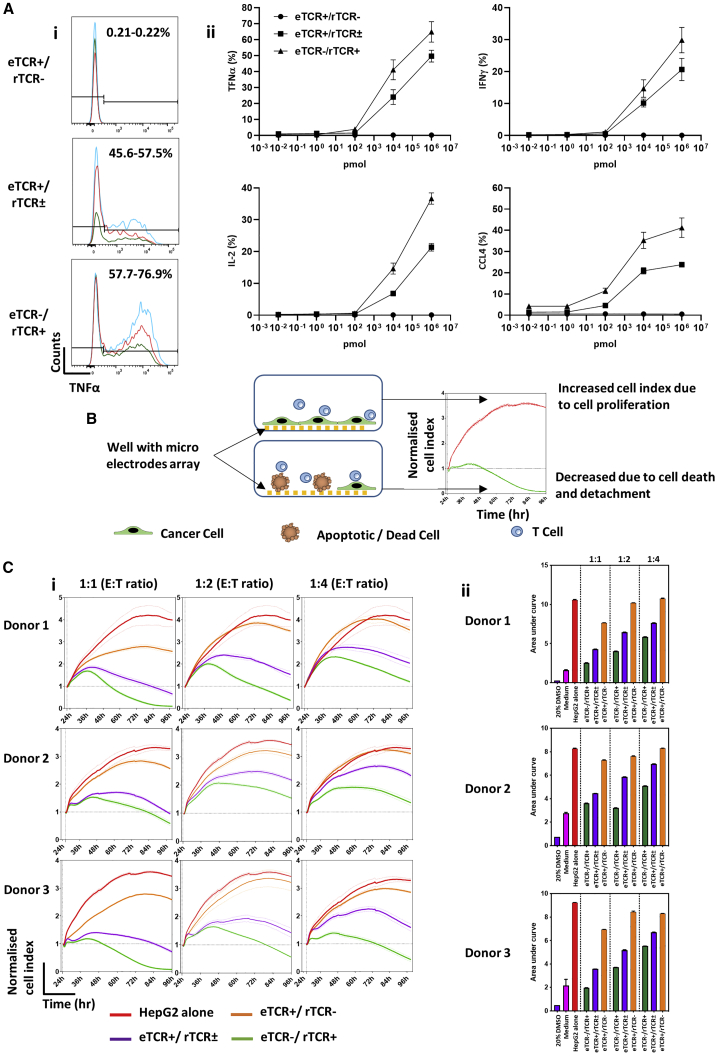
Figure 3.
Anti-HBV Responsiveness of eTCR+/rTCR±, compared to Base-Edited eTCR−/rTCR+ Effector T Cells
(A) Cytokine responses of effector T cells to the HepG2 cell line pulsed with target HBV surface peptide (S183-91, FLLTRILTI). n = 3. (i) Histograms of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) responses to HepG2 target cells pulsed with 1 μM target peptide. Both the eTCR+/rTCR± and eTCR−/rTCR+ effector groups are gated on CD45+ > CD3+ > rTCR+ > CD8+, whereas unmodifed eTCR+/rTCR− effectors are gated on CD45+ > CD3+ > rTCR− > CD8+. The three different colors represent results from three donors. (ii) Cytokine responsiveness at different concentrations of target peptide (S183-91). HepG2 target cells were pulsed with 1 μM control peptide (C18-27) to ensure specificity of response, showing cytokine responsiveness comparable to that of the no-peptide control. Effector groups eTCR+/rTCR± and eTCR−/rTCR+ are gated on CD45+ > CD3+ > rTCR+ > CD8+, whereas unmodified cells are gated on CD45+ > CD3+ > rTCR− > CD8+. Error bars represent ±1 SEM. (B) Schematic depiction of the xCELLigence impedance assay showing cancer cells (green) seeded in wells with micro-electrode array (yellow) in the presence of effector T cells (blue). Where T cells recognize cancer cells, this leads to cell death (brown) and reduced impedance, resulting in lower cell index values and area under the curve (AUC). (C) xCELLigence data across different effector:target (E:T) ratios (1:1, 1:2, and 1:4). (i) Visualization of normalized cell index (NCI) over time; all donors showed an increased NCI with decreased E:T ratio. Both HepG2 alone (red) and eTCR+/rTCR− (orange) show steadily increasing NCIs over time, whereas the eTCR+/rTCR± (purple) and eTCR−/ rTCR+ (green) groups show an initially increased NCI followed by a marked decline. Normalized to time point prior to effector T cell addition. (ii) Summary data of AUC. Increased AUC values were observed at the lower E:T ratios, with eTCR−/ rTCR+ consistently presenting with the lowest AUC values. Error bars represent ±1 SEM. IFNγ, interferon γ; IL-2, interleukin-2; CCL4, C-C motif chemokine ligand 4.