Figure 2.
Glucose Deprivation Triggers GBM Cells Hydrolyzing TG/LDs to Support Cell Survival
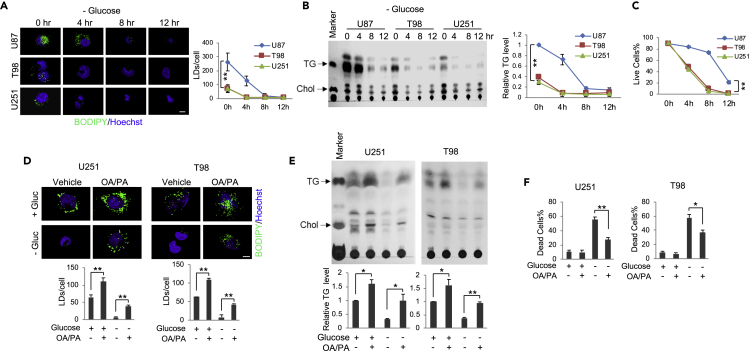
(A–C) U87, T98, and U251 GBM cells were cultured in medium with 25 mM glucose or no glucose for 4, 8, and 12 h. Cells were stained with BODIPY 493/503 (green)/Hoechst 33342 (blue) and observed by confocal microscopy (A). Quantification of LDs/cell for over 30 cells was conducted using the ImageJ software (mean ± SD). Total lipids were extracted and analyzed by TLC (B). TG levels at different time points and in various cell lines were normalized to U87 cells cultured in 25 mM glucose medium (mean ± SD, n = 3). Live cell percentage at different time points after glucose withdrawal was determined after trypan blue staining (mean ± SD, n = 3) (C). Significance between different cell lines was determined by two-way ANOVA. ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗p < 0.01. Chol, cholesterol.
(D–F) U251 and T98 cells were cultured in medium with/without palmitic acid (PA, C16:0, 5 μM) and oleic acid (OA, C18:1, 5 μM) mixtures (1:1) for 24 h and then placed in fresh medium in the absence or presence of glucose (Gluc, 25 mM) for 4 h. Cells were stained with BODIPY 493/503 (green)/Hoechst 33342 (blue) and observed by confocal microscopy (D). Quantification of LDs/cell in over 30 cells was conducted using ImageJ (mean ± SEM). Total lipid extracts from these cells were analyzed by TLC (E). Relative TG levels were quantified by ImageJ and normalized to the control cells (mean ± SD, n = 3) (E). Cell death was determined by trypan blue exclusion (mean ± SD, n = 3) (F).
Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05. Please also see Figure S1B.