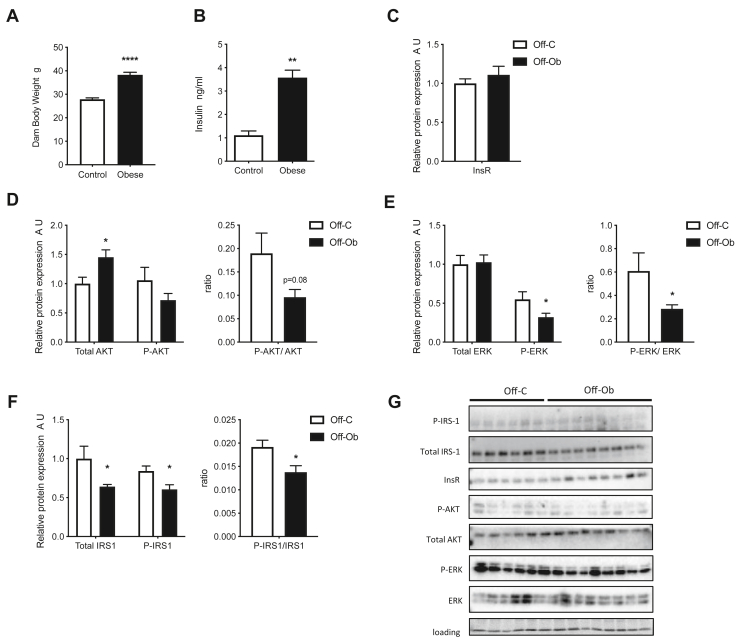
Figure 2.
Maternal obesity impacts on fetal hypothalamic insulin signalling pathways. A) Maternal body weight (g) and B) fed serum insulin levels (ng/ml) on embryonic day 13 (n = 4–7) C) Expression of InsR protein in fetal hypothalamus (A.U., expressed as relative to Off-C; n = 6–8) D-F) Expression of total protein and phosphorylated protein (A.U., expressed as relative to Off-C) and the ratio of phosphorylated/total protein for AKT, ERK and IRS1 (n = 6–8) G) Images of western blots represented by graphs in Figure 2 plus loading control. A-B) Control dam = white bars, Obese dam = black bars. C–F) Off-C = white bars, Off-Ob = black bars. b chow = black bars, Off-C HFD = white patterned bars, Off-Ob HFD = black patterned bars. Data are presented as mean +/− SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Outlier was excluded from (B) control (Grubb's method, alpha = 0.2, G = 1.493, outlier excluded value = 6.621).