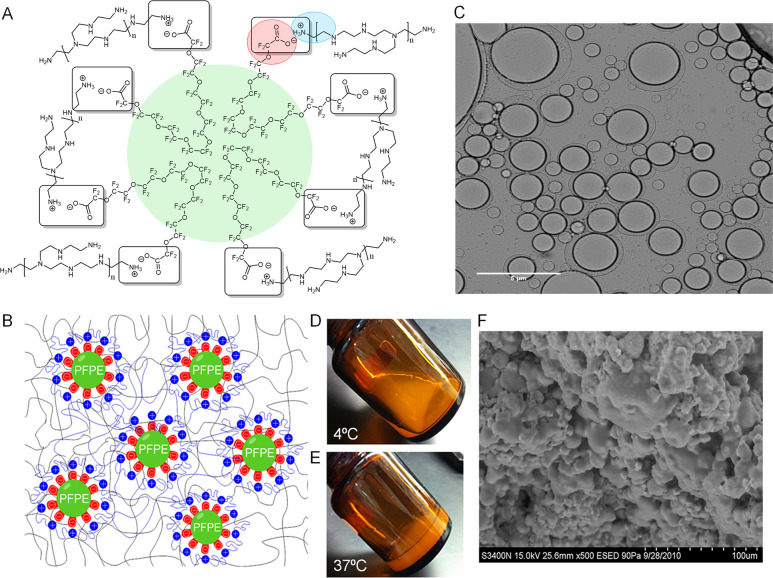
Figure 1.
(A) Structural schematic of the ionic interaction of PFPE carboxyl ion end groups, which are released following PFPE-Ester hydrolysis in aqueous medium, and ionized quaternary groups on exposed chains of branched 25 kDa PEI, resulting in ammonium salt bridges responsible for droplet surface stabilization at the PFPE/water interface. (B) Schematic representation of PFPE ionic surface cross-linked interaction with PEI in F127 hydrogel matrix. (C) Cross polarized optical microscopy image of the surface interaction where PFPE droplets are surrounded by PEI in aqueous medium, 50× magnification. (D–E) PFPE/PEI/F127 hydrogel thermoresponsive behavior. Sol state at 4 °C and gel state at body temperature (37 °C). (F) Scanning electron microscopy image of lyophilized cross-linked PFPE/PEI/F127 hydrogel, showing large and small droplets of PFPE oil dispersed into F127 matrix.