Figure 6.
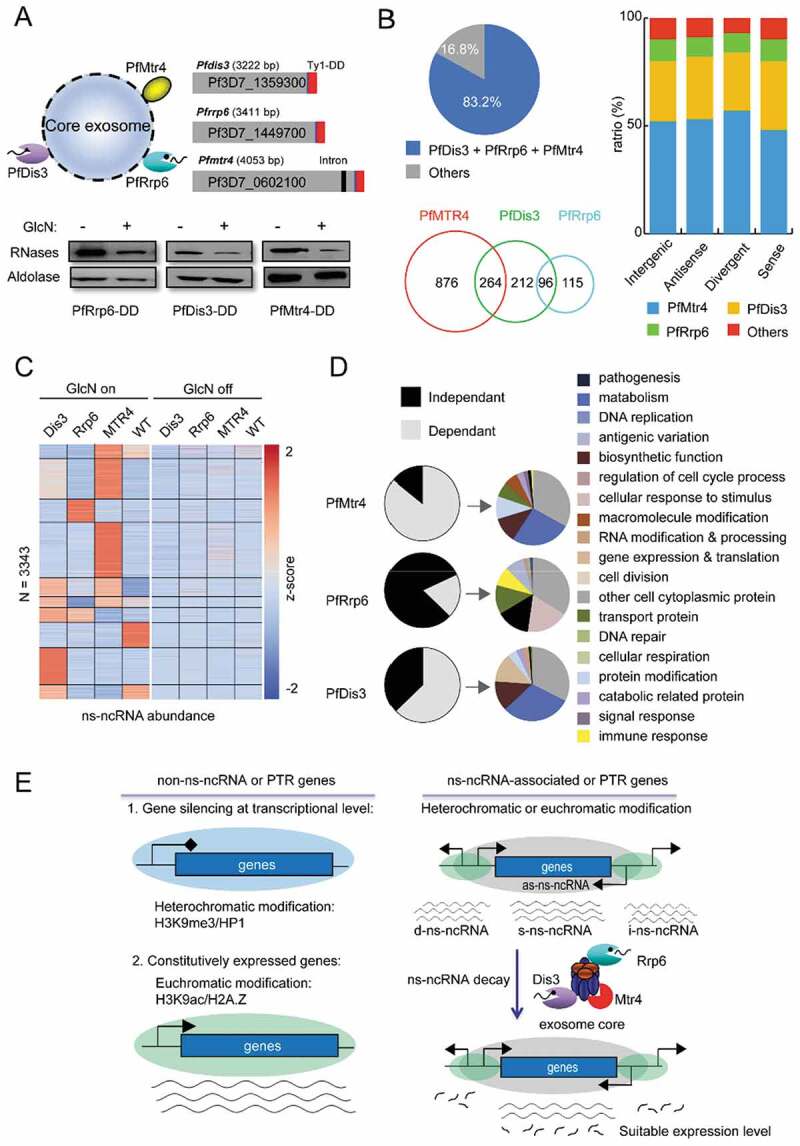
RNA exosome-mediated ns-ncRNAs degradation in P. falciparum. (A) Upper: the schematic representation of RNA exosome composition containing two catalytic subunits and another TRAMP-associated Mtr4 (left) and transgenic constructs of gene knock-down of Pfdis3, Pfrrp6, and Pfmtr4, respectively (right). The C-terminal fusion sequences are of the Ty1 epitope with triple repeats and glms ribozyme in tandem, and western blot analysis of gene knock-down effect for each exosome-associated subunits. (B) The ratio between lncRNAs regulated by exosome-associated subunits (Pfdis3, Pfrrp6 and Pfmtr4) and ns-ncRNAs at ring stage (pie chart); and Venn diagram showing the counts of ns-ncRNAs regulated by individual exosome-related subunits, respectively. The percentages of ns-ncRNAs regulated by different exosome-related genes (Pfdis3, Pfrrp6 and Pfmtr4) at TP10 for different ns-ncRNAs groups as shown in Fig. 2A. (C) Expression profiles of lncRNAs in Pfdis3-DD, Pfrrp6-DD and Pfmtr4-DD strains with drug (left) or without drug (right). (D) The percentages and GO enrichment of genes regulated by ns-ncRNAs dependently (grey) or independently (black) on Pfmtr4, Pfrrp6, and Pfdis3 pathways respectively; (E) Model of the putative regulatory functions of ns-ncRNAs for expression of post-transcriptional regulation-related genes and non-post-transcriptional regulation genes.
