Figure 2.
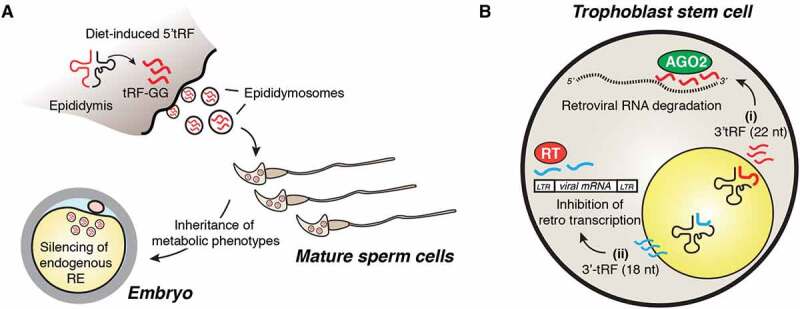
tRF function in epigenetic silencing during early embryogenesis. (A) tRFs mediate intergenerational transmission of metabolic phenotypes. 5ʹ-tRFs including tRF-GG, exhibit a two-three fold increase in somatic epididymis cells upon dietary restriction and are transferred to maturing sperm cells. This process has been proposed to repress endogenous retroelements (RE) and pass paternal inherited information during embryonic development. (B) Murine trophoblastic stem cells produce 3ʹ-tRFs that inhibit the replication of endogenous retroviruses via two distinct mechanisms: (i) putative model illustrating 22 nt 3ʹ-tRFs inducing post-transcriptional silencing of retroviral RNA possibly via association with the canonical miRNA-effector protein AGO2. (ii) 18 nt 3ʹ-tRFs interfere with reverse transcription of viral RNAs to restrict transposon mobility.
