Figure 7.
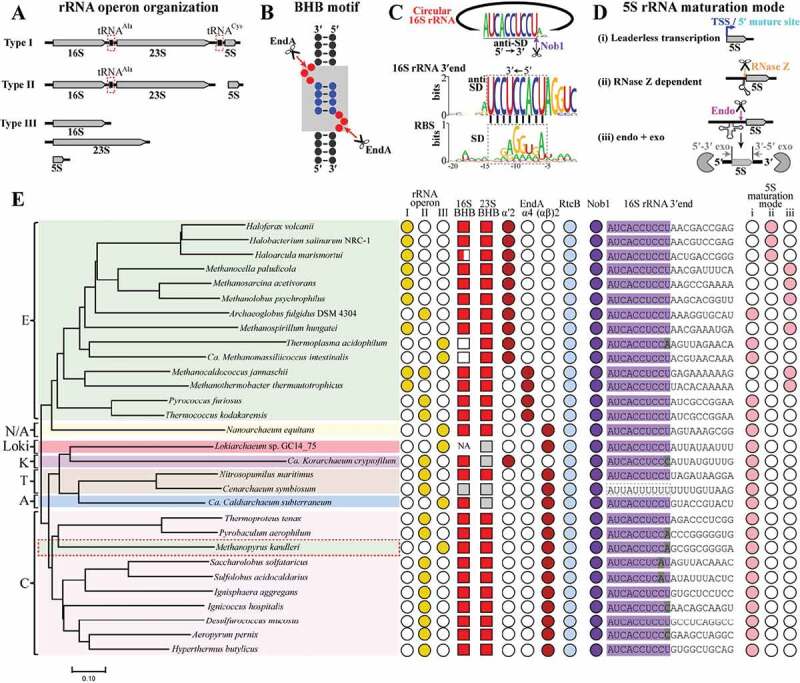
The conserved rRNA maturation modes in archaea. By searching the available archaeal genomes in KEGG database, key elements involved in pre-rRNA processing and maturation were analysed in 30 representative species affiliating to the four superphyla of archaea. These include three organization patterns of rRNA operons (a), 16S and 23S rRNA BHB motifs (b), 16S 3′ end sequences cleaved by Nob1 (c), three maturation modes of 5S rRNA (d), and the presence of EndA, RtcB and Nob1 (e). The grey shadowed BHB motif in (B) consists of two bulges (red spheres) and an in-between helix (blue spheres). A conserved 3′ end sequence of 16S rRNA noted as anti-SD in (C) is found in almost all of the investigated archaea, and perfectly complementary to the M. psychrophilus SD sequence (black dot line framed). Three maturation modes of 5S rRNA are summarized in the 30 investigated archaeal species (d,e): (i) transcribed as matured ‘leaderless’ 5S rRNA prevalent in TACK, Asgard and DPANN, (ii) RNase Z-dependent maturation on a tRNA-like structure widely distributed in haloarchaea, and (iii) ‘endo+exo’ mode employed in methanoarchaea. A representative phylogenetic tree (e) is constructed on the homology analysis of the protein concatenation of EndA and Nob1 from the 30 investigated archaeal species. The tree was constructed using MEGA7.0, and the bar represents 10% sequence difference. E, Euryarchaeota (green background); T, Thaumarchaeota (brick red background); A, Aigarchaeota (blue background); C, Crenarchaeota (pink background); K, Korarchaeota (magenta background); N/A, Nanoarchaeota and ARMAN (yellow background). Distributions of the key elements involved in rRNA maturation are shown at the right side. Filled and empty symbols represent the presence and absence of items in corresponding archaeal species. Grey filled squares indicate incomplete or inaccurate 16S or 23S rRNA sequences that do not allow a prediction of BHB motif, and NA means no available 16S or 23S rRNA sequence in the database. Grey shaded letters in 3′ end of 16S rRNA indicate mutated sites by comparing with the conserved mature 3′ end sequence shown in (C).
