Figure 2.
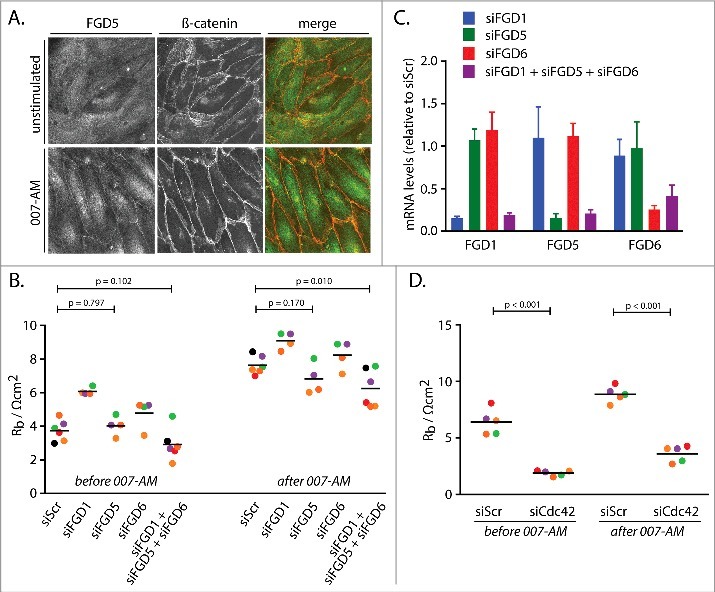
Cdc42GEFs of the FGD family and Cdc42 mediate Rap1-induced barrier function. (A) Immunofluorescence of HUVEC monolayers either not stimulated or stimulated with 007-AM 15 minutes prior to fixation. The cells were stained for FGD5 and β-catenin. The merged image depicts FGD5 in green and β-catenin in red. (B) Endothelial barrier (Rb) of control HUVEC monolayers (siScr) and HUVEC monolayers depleted of FGD1 (siFGD1), FGD5 (siFGD5), FGD6 (siFGD6) or the three FGDs combined (siFGD1 + siFGD5 + siFGD6), either before or 45 minutes after stimulation with 1 µM 007-AM. Different colors represent independent experiments (n > 3). Averages are indicated by the black lines. (C) mRNA levels of FGD1, FGD5 and FGD6 in HUVEC monolayers depleted of FGD1 (siFGD1, blue bars), FGD5 (siFGD5, green bars), FGD6 (siFGD6, red bars) or the three FGDs combined (siFGD1 + siFGD5 + siFGD6, purple bars), represented as expression relative to monolayers transfected with a control siRNA. The bars show averages of independent experiments (n = 4). Error bars indicate standard deviation. (D) Endothelial barrier (Rb) of control HUVEC monolayers (siScr) and HUVEC monolayers depleted of Cdc42 (siCdc42), either before or 45 minutes after stimulation with 1 µM 007-AM. Different colors represent independent experiments (n = 5). Averages are indicated by the black lines. Knockdown efficiencies are shown in supplemental figure 1B.
