Figure 3.
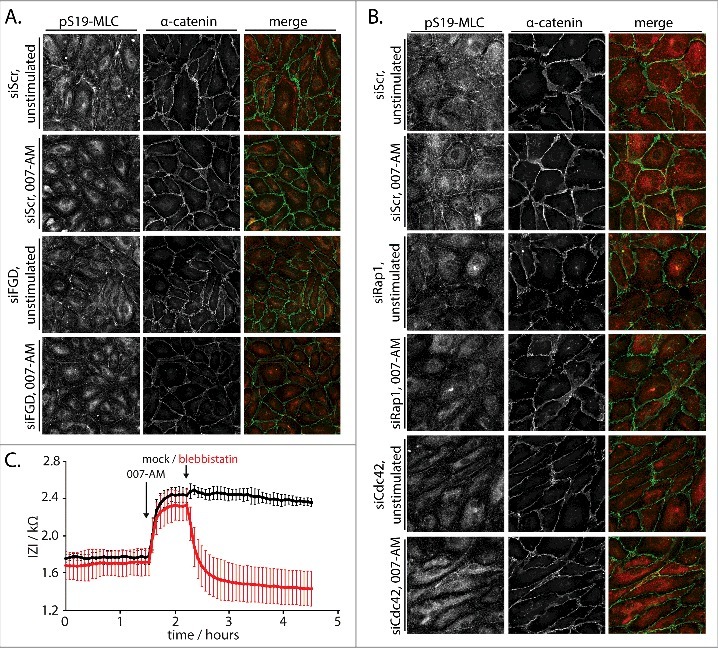
Rap1 induces Cdc42-dependent junctional tension to enhance barrier function. (A) Immunofluorescence of HUVEC monolayers transfected with control siRNA (siScr) or siRNAs targeting FGD1, FGD5 and FGD6 (siFGD), either not stimulated or stimulated with 1 µM 007-AM 15 minutes prior to fixation. The cells were stained for pS19-MLC and α-catenin. The merged image depicts pS19-MLC in red and α-catenin in green. Knockdown efficiencies are shown in supplemental figure 1C. (B) Immunofluorescence of HUVEC monolayers transfected with control siRNA (siScr), siRNAs targeting Rap1A and Rap1B (siRap1) or siRNA targeting Cdc42 (siCdc42), either not stimulated or stimulated with 1 µM 007-AM 15 minutes prior to fixation. The cells were stained for pS19-MLC and α-catenin. The merged image depicts pS19-MLC in red and α-catenin in green. Knockdown efficiencies are shown in supplemental figure 1D. (C) Real-time measurement of the endothelial barrier of HUVEC monolayers. Absolute values of the impedance (Z) at 4000 Hz are plotted over time. 1 µM 007-AM was added to all wells when indicated, followed by mock (black line) or 100 µM Blebbistatin (red line) treatment as indicated. The lines show average values of four technical replicates within one representative experiment. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
