Figure 4.
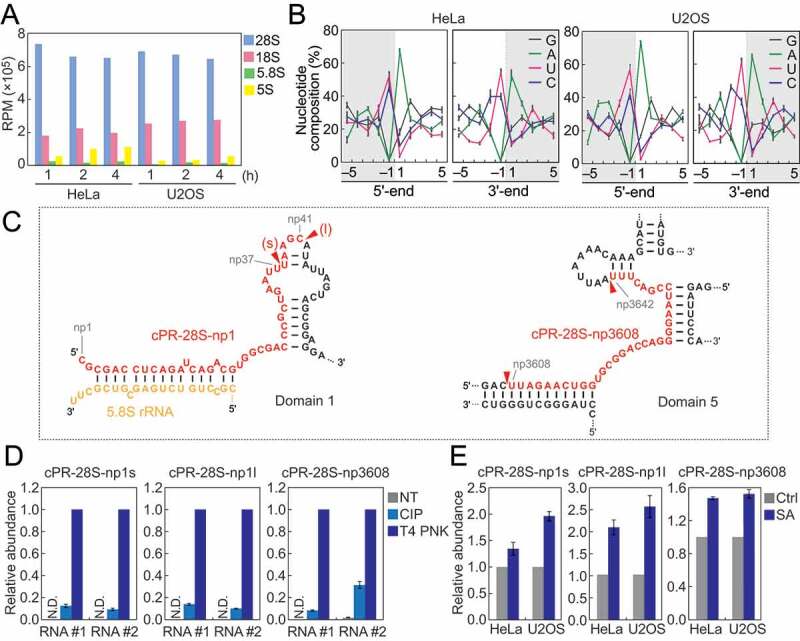
Analyses of rRNA-derived cP-RNAs.
(A) Reads per million (RPM) of cP-RNAs mapped to the indicated rRNAs. (B) Nucleotide compositions around the 5′- and 3′-ends of rRNA-derived cP-RNAs. A dashed line separates upstream and downstream positions for the 5′-and 3′-ends, representing the cleavage site that generates rRNA-derived cP-RNAs (the regions outside of cP-RNA-generating regions are colored in grey). (C) The regions from which the indicated cP-RNAs were derived are shown in red in the secondary structure of substrate rRNAs. The secondary structures are according to [40,41]. (D) The total RNA from SA-treated (2 h) HeLa cells were treated with CIP or T4 PNK and subjected to TaqMan RT-qPCR for detection of the indicated rRNA-derived cP-RNAs. The amounts from T4 PNK-treated RNA were set as 1, and relative amounts are indicated. Averages of three technical replicates with SD values are shown. NT: a non-treated sample used as a negative control. N.D.: not detected. #1/#2: biological replicates. (E) The total RNA from HeLa or U2OS cells treated with SA or water (control) for 2 h were subjected to TaqMan RT-qPCR for detection of the indicated rRNA-derived cP-RNAs. The amounts from control cells were set as 1, and relative amounts are indicated. Averages of three experiments with SD values are shown.
