Figure 3.
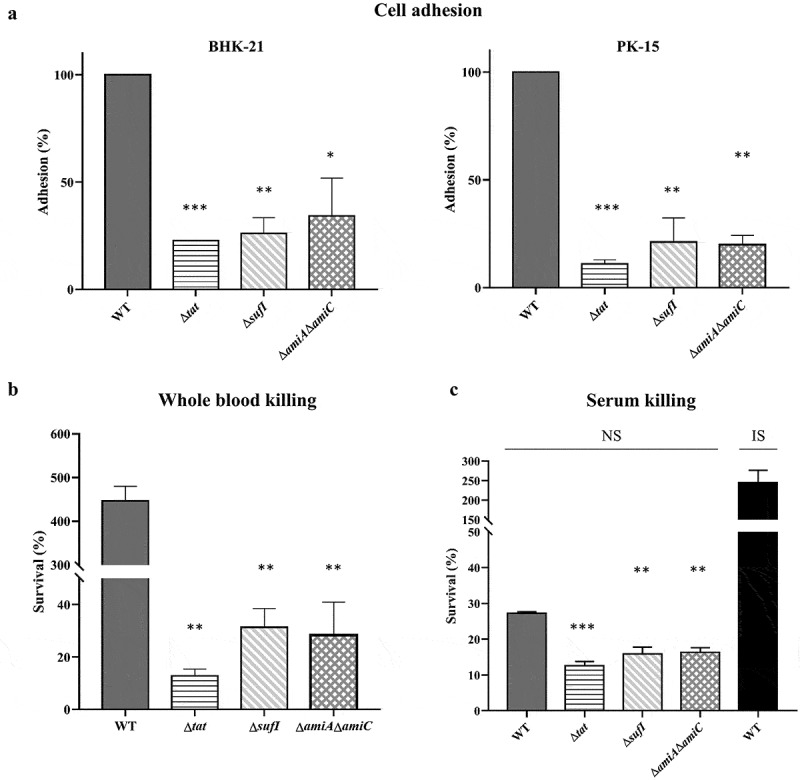
In vitro cell adhesion, and whole blood and serum bactericidal assays. (a). In vitro cell adhesion.
PK-15 cells and BHK-21 cells grown in 6-well plates were infected with cells of each indicated bacterial strain grown to mid-log phase with a ratio of 10:1 followed by incubation at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 2 hours. The cells were then washed with PBS and lysed with sterile water. The input bacterial cells and the cell lysates were then diluted and plated onto LB plates for bacterial enumeration. The adhesion rate of the WT strain was set as 100%. (b). Whole blood bactericidal assay. Bacterial cells of each indicated strain grown to mid-log phase were incubated with heparinized mouse whole blood at 37°C for 1 hour. The initial input and the incubated samples were then diluted and plated onto LB plates for bacterial enumeration. (c). Serum blood bactericidal assay. Bacterial cells of each indicated strain grown to mid-log phase were incubated with normal mouse serum (NS) at 37°C for 1 hour. A control in which the WT strain was incubated with heat-inactivated serum (IS) was performed in parallel. The samples were then diluted and plated onto LB plates for bacterial enumeration. The initial input and the incubated samples were then diluted and plated onto LB plates for bacterial enumeration. The assays were performed in triplicate. The survival rate was calculated as (CFUrecovered/CFUinput) × 100. * represents p value <0.05; ** represents p value <0.01, *** represents p value <0.0001.
