Figure 1.
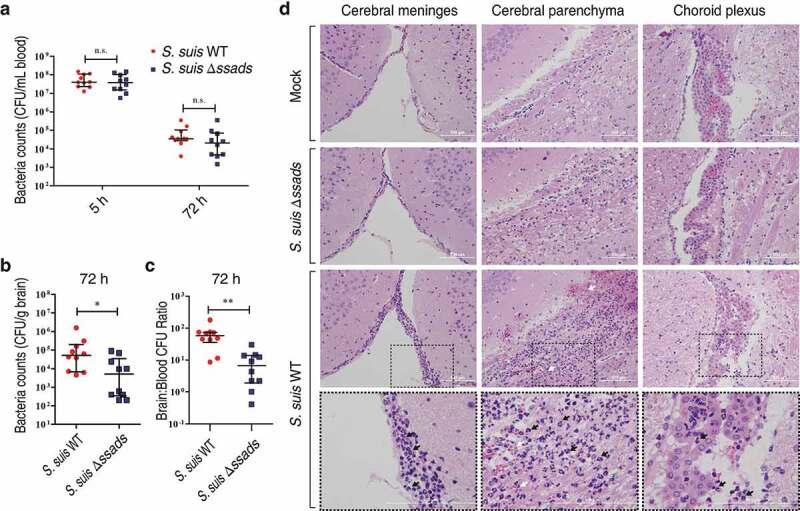
Ssads gene deficiency impedes S. suis entry into mouse brains. (a–c) Six-week-old female C57BL/6 mice were infected i.p. with approximately 5 × 106 CFU of the S. suis WT strain 05ZYH33 (n = 10), the ssads-deficient mutant Δssads (n = 10), or sterile THY media (n = 3). Bacterial counts in the blood (CFU/mL blood) at 5 h and 72 h post-infection (a) and brain (CFU/g tissue) at 72 h post-infection (b) were determined. (c) After correction for blood contamination using CFU in blood and a conservative estimate of the mouse cerebral blood volume (2.5 mL per 100 g tissue), the ratio of brain:blood CFU at 72 h post-infection was determined. Horizontal lines and error bars denote the median and IQR, respectively. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U test. (d) Histopathology of representative brain tissues from mice injected with THY media (Mock), infected with S. suis WT strain or infected with the Δssads mutant. Dotted box regions are magnified to better indicate hemorrhage (white arrows) and polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration (black arrows). Scale bar indicates 100 µm.
