Figure 2.
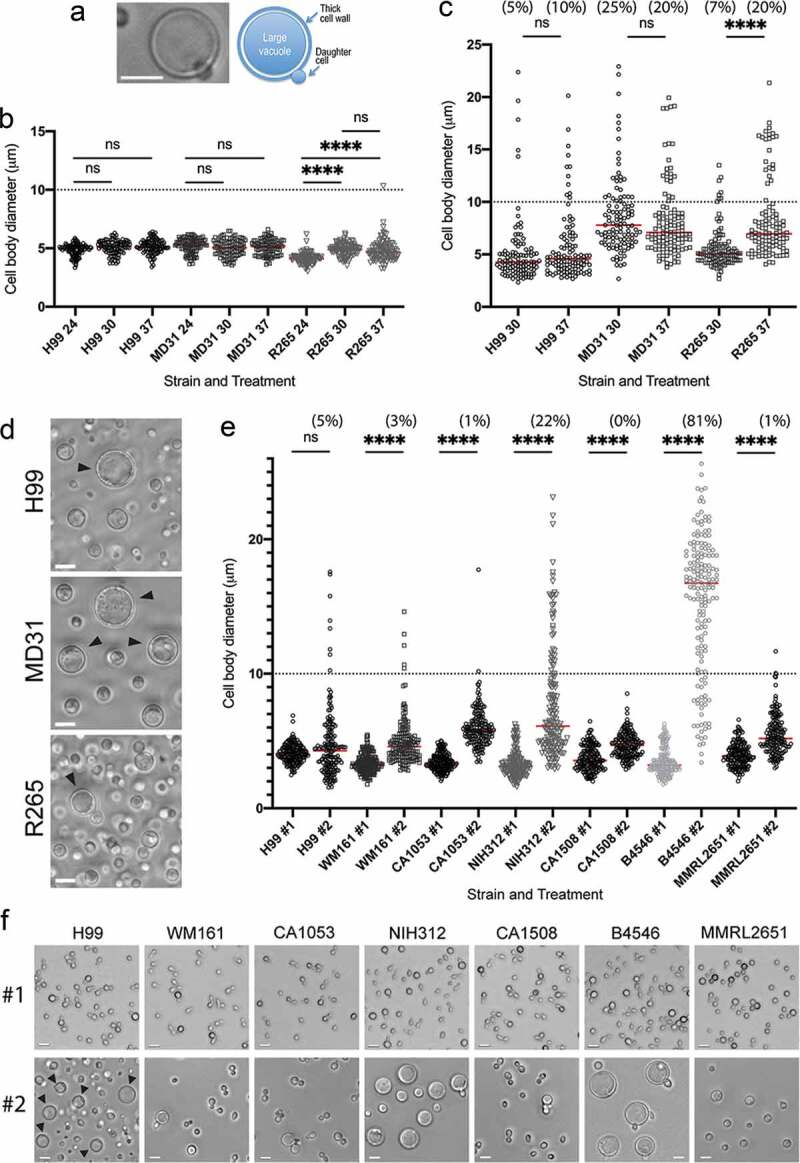
Titan cell formation among the C. neoformans and C. gattii species complex.
(a) Features of a Titan cell as observed with the DIC microscopy. C. neoformans var. grubii (strain H99) was grown under titanization conditions according to Dambuza et al. [33] at 30°C for 5 days. (b) The effect of temperature (24, 30, and 37°C) on cell diameter of two C. neoformans strains (H99 and MD31) and C. deuterogattii (R265). Cells were incubated in YPD for 24 hours prior to imaging. (c) The effect of 37°C as compared to 30°C on the median cell diameter under titanization conditions [33] for C. neoformans (H99, MD31) and C. deuterogattii (R265). (d) Representative images illustrating cells incubated at titanization conditions [33] at 30°C, whose diameters are plotted in C. (e) The effect of incubation under titanization conditions [33] at 30°C for 5 days (marked as #2) on cell body diameter of C. neoformans (H99) and representative strains of the C. gattii species complex. Cells were grown in YPD at 30°C for 8 hours as control (marked as #1). (F) Images of cells whose diameters are plotted in E (#1 – YPD control, #2 – titanization conditions at 30°C for 5 days). The number of cells counted for each condition were 100 (in b), 110 (;in c), and 167 (in e). The numbers above each plot in C and E represent the percentage of cells with the diameter above 10 μm. Statistical significance of the difference in the mean cell diameter is indicated as follows: ns (not significant), **** (p < 0.0001) Bars in (a, d), and (f) represent 10 µm.
