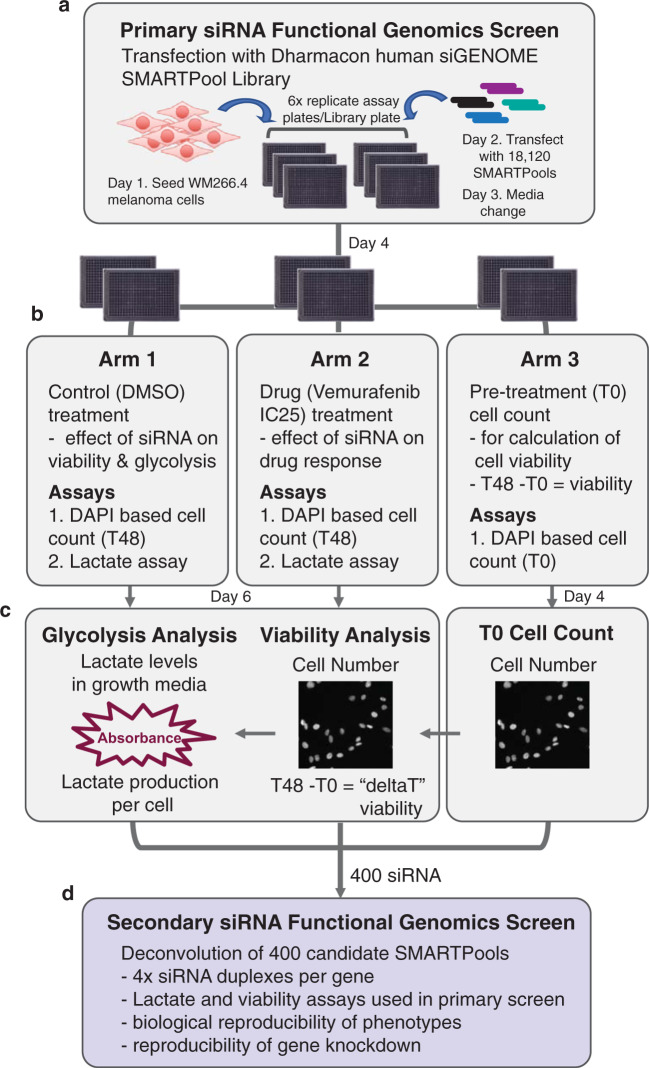
Fig. 1.
Overview of the multiparametric genome wide siRNA screening approach. (a) Experimental scheme for the genome wide siRNA screen to identify genes that regulate cell viability and glycolysis, in the presence and absence of the BRAF inhibitor (BRAFi) vemurafenib. WM266.4 cells were forward transfected with siRNA SMARTpools 72 h prior to assessment for glycolytic capacity and cell viability. The primary screen assessed siRNA SMARTpools targeting 18,120 protein-coding genes (see Data Record 111). (b) The screen consisted of 3 arms: 1. Control (DMSO) treatment arm to assess effect of gene knockdown on cell viability and glycolysis, and identify BRAFi specific effects; 2. Drug (vemurafenib) treatment arm to assess effect of gene knockdown on BRAFi response; and 3. Pre-treatment arm to calculate cell number prior to treatment (T0) for calculation of cell viability (T48 – T0 = deltaT). (c) Functional assays used to determine lactate production per cell and cell viability, in the presence or absence of BRAFi. Automated image analysis was used for cell nuclei counts to determine cell number. The lactate assay is an enzymatic based assay performed on growth media, and absorbance values were normalised to cell number to calculate lactate production per cell. Wells that were identified as ‘Low Cell Density’ were excluded from lactate analysis. (d) 400 candidate siRNA SMARTPools were selected for validation in a secondary deconvolution screen, whereby the 4 individual siRNA duplexes that comprise the SMARTPools were arrayed into individual wells (see Data Record 212).