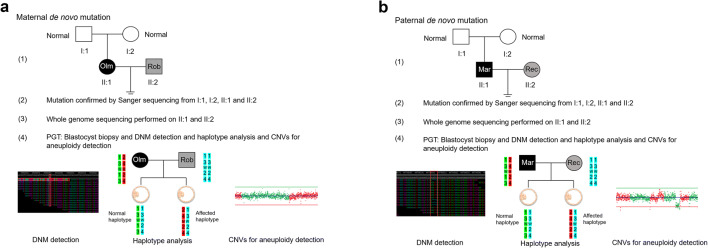
Fig. 1.
Workflow of preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) for de novo mutations (DNMs) of different origins. a Maternal DNM combined with paternal Robertsonian translocation. (1) pedigree in two generations. Filled symbols represent affected individuals (black indicates patient with the monogenetic disease and gray indicates patient with the chromosomal disease); open symbols represent unaffected individuals. Circles and squares indicate females and males, respectively; (2) mutation (c.1246C>T) confirmed by Sanger sequencing from I:1, I:2, II:1, and II:2; (3) whole-genome sequencing (WGS) performed on all 4 family members to identify the most informative single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers for PGT; (4) PGT by blastocyst biopsy for combined mutation, and haplotype and copy number variation (CNV) analysis; haplotype construction is based on maternal heterozygous and paternal homozygous sites. In the haplotype, the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 indicate different SNP markers, such as A, T, C, and G; the letter W indicates the wild-type allele, and the letter M indicates the mutant allele. b Paternal DNM combined with maternal reciprocal translocation. (1) Pedigree in two generations. Filled symbols represent affected individuals (black indicates patient with the monogenetic disease and gray indicates patient with the chromosomal disease), and open symbols represent unaffected individuals. Circles and squares indicate females and males, respectively; (2) mutation (c.4952_4955delAATG) confirmed by Sanger sequencing from I:1, I:2, II:1, and II:2; (3) WGS performed on all 4 family members to identify the most informative single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers for PGT; (4) PGT by blastocyst biopsy for combined mutation, and haplotype and CNV analysis; haplotype construction is based on paternal heterozygous and maternal homozygous sites. In the haplotype, the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 indicate different SNP markers, such as A, T, C, and G; the letter W indicates the wild-type allele, and the letter M indicates the mutant allele. Mar, Marfan syndrome; Olm, Olmsted syndrome; Rec, reciprocal translocation; Rob, Robertsonian translocation