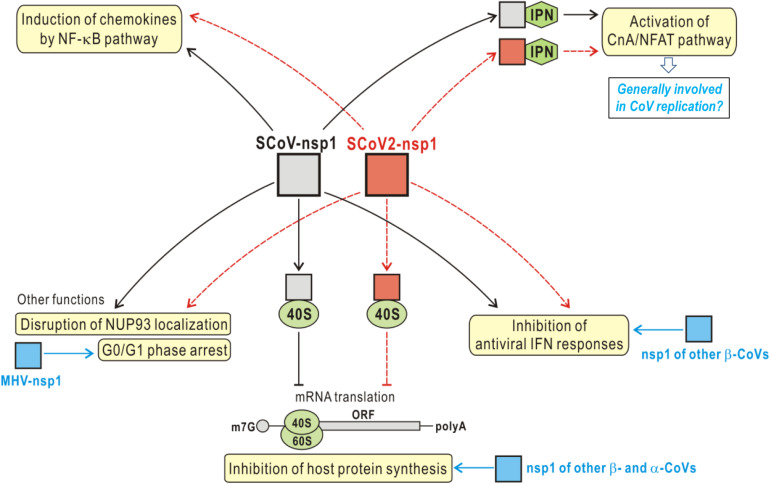
FIGURE 5.
Potential functions of nsp1. The reported functions of SARS-CoV nsp1 (SCoV-nsp1) include inhibition of host protein synthesis by binding to 40S ribosomal subunit, inhibition of antiviral IFN responses, activation of CnA/NFAT signaling by interacting with immunophilins (IPN), induction of chemokines, disruption of NUP93 localization, and induction of cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase (summarized in the yellow textboxes). Notably, some of these functions are shared by the nsp1 of other representative CoVs (indicated in blue), despite the low sequence identifies of the nsp1 proteins. In addition, the cellular CnA/NFAT pathway also seems to be generally involved in CoV replication, as inhibition of the pathway could block the replication of not only SARS-CoV (β-CoV), but also the CoVs from other genera. Given the high sequence identity and the possible structural similarity, SARS-CoV-2 nsp1 (SCoV2-nsp1) likely has the activities similar to those of SCoV-nsp1, which merit systematic investigations in the future for better understanding of the viral infection and pathogenesis and development of drugs or vaccines. See also the descriptions in the text.