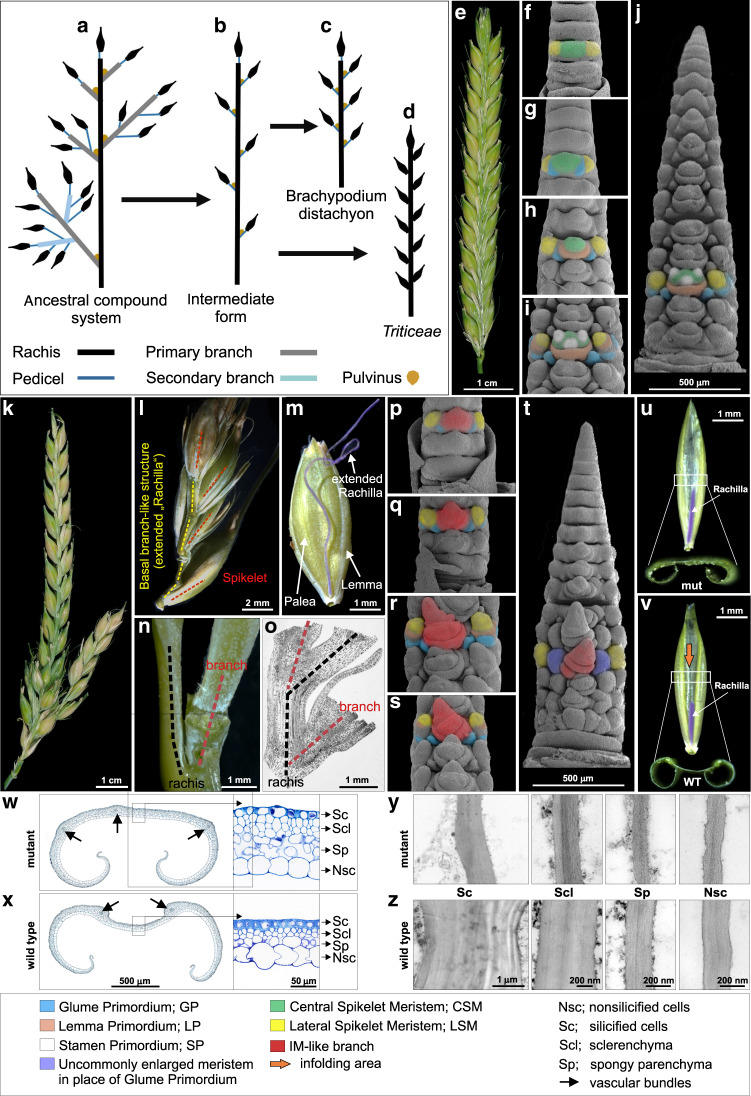
Fig. 1. Proposed evolutionary pattern of grass inflorescences, and barley spike/palea morphology in wild-type and com1.a mutant.
a–d Model for grass inflorescence evolution from ancestral compound form to spike in Triticeae; reprinted from Vegetti and Anton2 with kind permission from Elsevier. e Spike morphology of wild-type (Wt), two-rowed barley cv. Bowman. f–i SEM imaging of the early developmental stages in immature Wt spike; triple mound: TM (f) glume primordium: GP (g) lemma primordium: LP (h) and stamen primordium: SP (i). Images are taken from basal nodes where a single node is used for color coding. j Dorsal view of whole immature Wt spike at stamen primordium stage. k Branched spike of BW-NIL(com1.a) mutant at maturity. l, m Depicted is a small, spike-like branch structure, arisen from the central spikelet position due to loss of CSM identity, from intense (l) to weak appearance as an extended (ext.) rachilla (m), M also depicts a developing grain enclosed by lemma and palea. n, o Lack of pulvinus at the base of a branch in BW-NIL(com1.a) mutant spike (n) supported by histological imaging (o). p–s Developmental stages of immature BW-NIL(com1.a) mutant spike from early GP (p), GP (q), to LP (r) and early SP (s) taken from the basal nodes. t Dorsal view of whole immature BW-NIL(com1.a) mutant spike at early stamen primordia. u Longitudinal adaxial view of the palea in BW-NIL(com1.a); white rectangle corresponds to the area used to take sections for histological analysis and to the lower image depicting the flat-plane surface of a palea cross section. mut stands for mutant (v) Longitudinal adaxial view of the palea in Wt; the lower image corresponds to the infolding surface of a palea cross section. w, x Histological analyses of transverse sections (from u, v; white rectangles) of the palea in BW-NIL(com1.a) (w) and Wt (x). Paleae are from spikelets shortly before anthesis. y, z TEM based imaging of walls of paleae cells in BW-NIL(com1.a) (y) versus Wt (z).