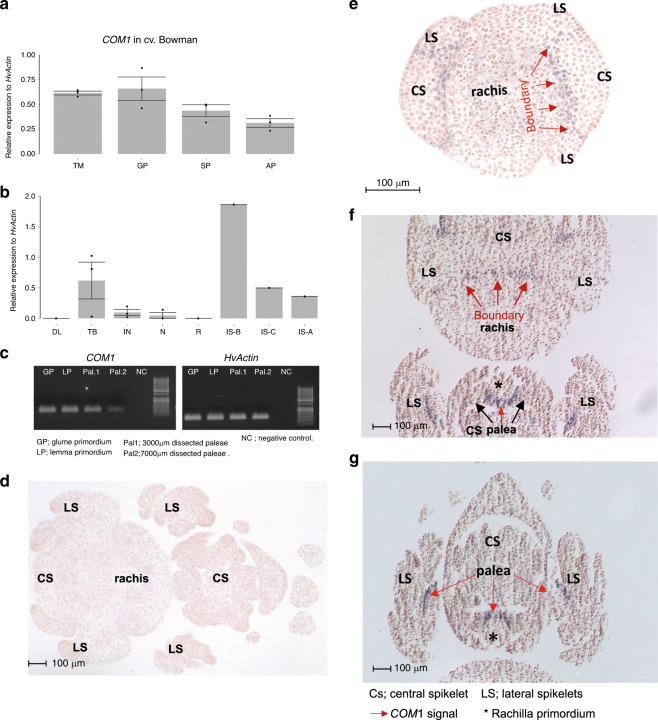
Fig. 7. Transcript analyses of COM1 in two-rowed barley.
a Relative COM1 expression at different stages of immature barley spike, including TM, GP, SP, and awn primordium (AP, a stage following stamen primordium18) in cv. Bowman. Data are generated from three biological replicates from 15–25 plants; mean ± SE are reported. b Relative COM1 expression in different organs (DL; developing leaf, TB; tiller buds, IN; culm internode, N; culm node, R; Root) along with spike sections (IS-B; immature spike basal nodes, IS-C; immature spike central nodes, IS-A; immature spike apical nodes) at AP stage in cv. Bowman. Despite expression in tiller buds, no differences in tiller number was observed (Supplementary Fig. 4). Dev leaf and IM stands for developing leaf and inflorescence meristem, respectively. Data are generated from three biological replicates from 15–25 plants; mean ± SE are reported. Note that only one biologically independent experiment was performed for IS (a–c). c Semi-qPCR of COM1 (left) and HvActin (right) mRNAs in two different stages of immature spike development, GP and LP (as positive controls), as well as in two palea samples. 50 bp Plus DNA ladder was used. d COM1 mRNA in situ control hybridization using pooled sense probes. e–g mRNA in situ hybridization of COM1 using pooled anti-sense probes. Tissues represent cross-section through a spikelet triplet at TM (e) and AP stages (f–g) of barley cv. Bonus (a two-rowed Wt). Source data underlying (c, d–g) are provided as a Source data file.