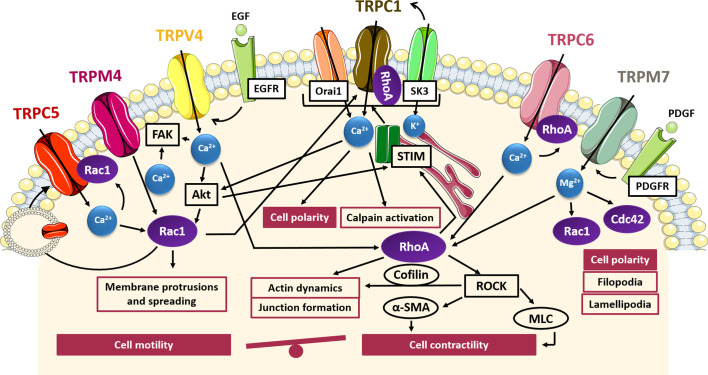
Figure 1.
TRP- small GTPases signaling pathways interplay in cell migration. Cartoon depicting TRP channels signaling pathways affecting cell motility and contractility through GTPases. TRPC5, TRPM4 and TRPV4 induce the formation of protrusions and spreading via Rac1 activation in a Ca2+-dependent manner and at the same time Rac1 promote the translocation of TRPC5 into the plasma membrane; Rac1 and RhoA through SOCE activation induce TRPC1-mediated cell polarization for directional cell migration; TRPM7 control polarized cell movement through the regulation of Rac1 and Cdc42 in a Mg2+-dependent way; TRPM7, TRPV4, and TRPC6 contribute to actin dynamics and cell contractility through the Mg2+- or Ca2+-mediated activation of RhoA/ROCK pathways. FAK, focal adhesion kinase; Akt, protein-kinase B; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; Orai1, calcium release-activated calcium channel; SK3, small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel 3; STIM, stromal interaction molecule 1; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; α-SMA, alfa-smooth muscle actin; MLC, myosin light chain.