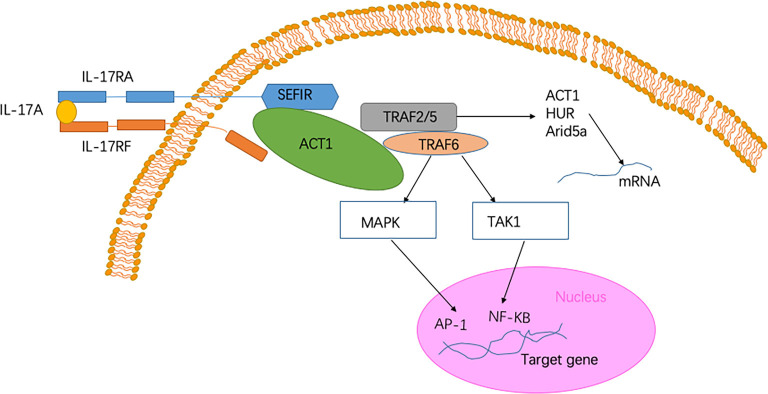
Figure 1.
Signaling pathway of Interleukin-17A (IL-17A). The heterodimer receptor consists of two subunits, IL-17RA and IL-17RF, which bind to IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-17AF ligands. The intracellular SEF/IL-17 receptor (SEFIR) domains interact with a corresponding SEFIR motif on the Act1 adaptor (Novatchkova et al., 2003). TNF-receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and TRAF2/5 proteins bind to the TRAF-binding site in Act1. After binding to Act1, TRAF6 mediates the activation of the classical nuclear factor-κB (NF-KB) pathway of MAPK:AP-1. Collectively, these pathways trigger the transcriptional induction of target genes (Qian et al., 2007). In the IL-17 signaling pathway, a pathway of post-transcriptional mRNA stabilization is promoted through the recruitment of TRAF2 and TRAF5 by Act1 (Schwandner et al., 2000). This physiological process is achieved by controlling multiple RNA-binding proteins, such as HuR and Arid5a.