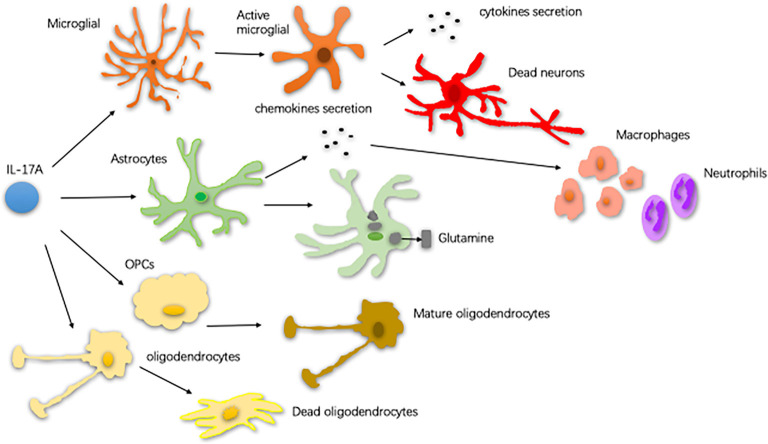
Figure 2.
The way of glial cells respond to IL-17A. In central nervous system (CNS) neurodegenerative diseases, IL-17A binds to the receptor on the surface of microglia and activates microglia. Activated microglia secrete cytokines, exacerbating dopaminergic neurons loss. Astrocytes respond to IL-17A through generating chemokines to promote the recruitment of inflammatory cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils. IL-17A reduces the ability of astrocytes to absorb and transform glutamate as well as enhance the excitotoxicity of glutamate. IL-17A inhibits the maturation of oligodendrocyte lineage cells (OPCs) and exacerbates the TNF-α-induced oligodendrocyte apoptosis (Qian et al., 2007; Stromnes et al., 2008; Kang et al., 2010; Ji et al., 2013; Kang Z. et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2015; Rodgers et al., 2015; Liu Z. et al., 2019).