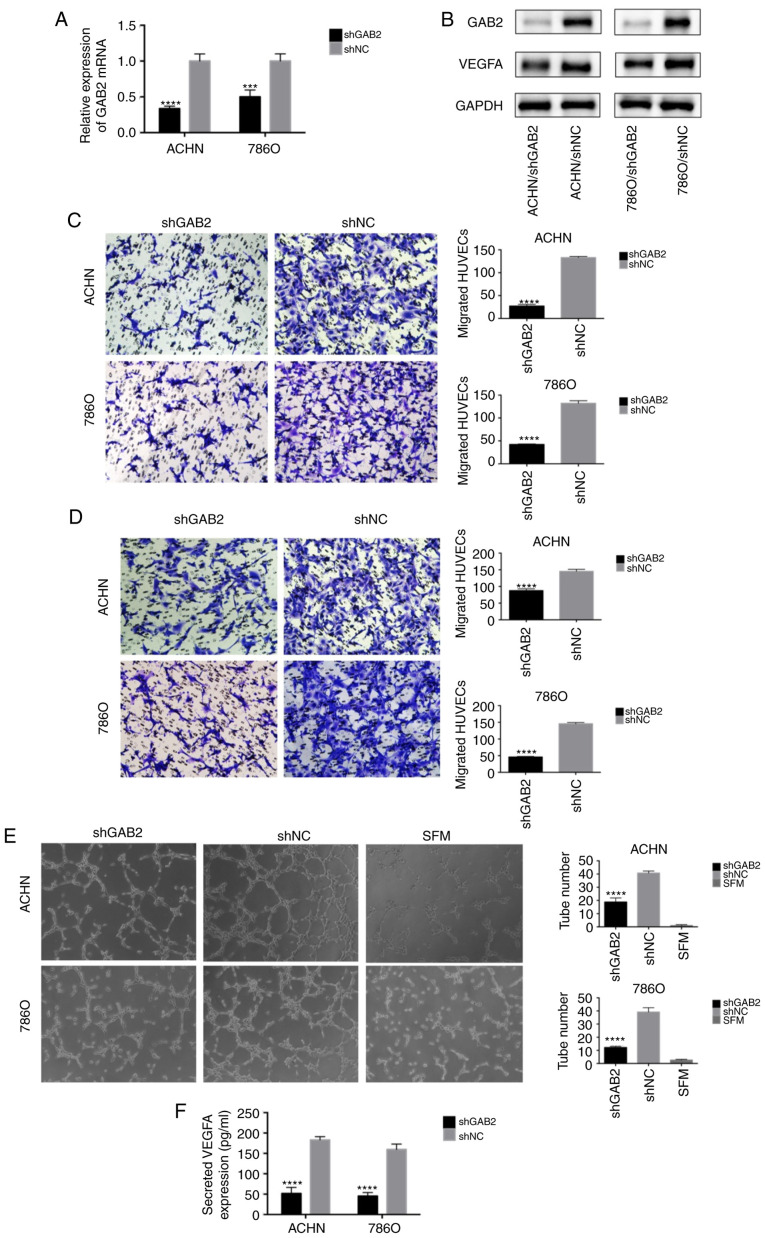
Figure 4.
GAB2 plays a crucial role in RCC angiogenesis. (A and B) Real-time PCR and western blot analysis were used to confirm the knockdown of GAB2 in ACHN and 786O cells transfected with LV-shGAB2 both at the mRNA and protein level. GAB2 knockdown decreased VEGFA at the protein level. ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001 compared to the shNC group. (C) GAB2 knockdown decreased the recruitment of HUVECs in a co-cultured system. Cancer cells that were cultured in the bottom of a 24-well plate were used to recruit HUVECs. ****P<0.0001 compared to the shNC group. (D) GAB2 knockdown decreased the recruitment of HUVECs through the conditioned medium (CM) collected from the ACHN, 786O/LV-shGAB2, and ACHN, 786O/LV-shNC cells. The migrated cells in six random fields per well were counted (magnification, ×200). ****P<0.0001 compared to the shNC group. (E) GAB2 knockdown reduced the tube formation of HUVECs diluted in SFM or CMs. The representative images of tube-like structures are shown, and the tube numbers in the whole field were counted (magnification, ×100). ****P<0.0001 compared to the shNC group. (F) The concentration of secreted VEGFA protein in the CMs was determined by ELISA. The values were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). GAB2, GRB2-associated binding protein 2; RCC, renal cell carcinoma; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; SFM, serum-free medium; CM, conditioned medium; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A.