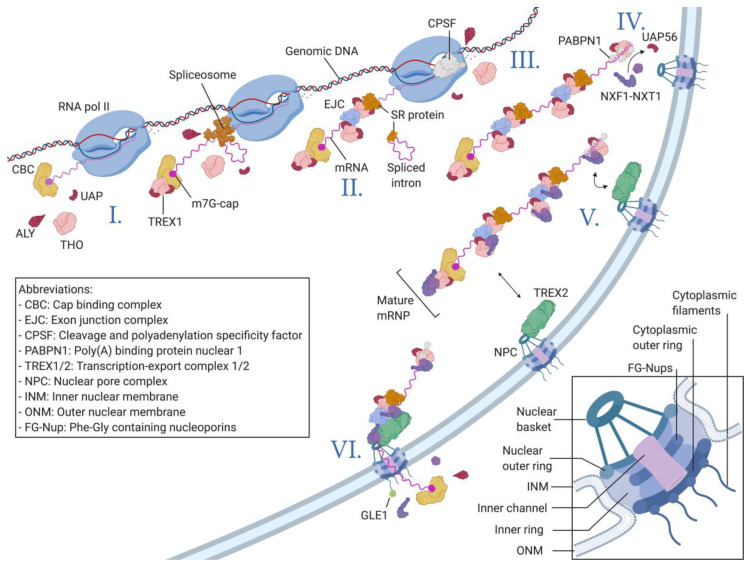
Figure 1.
The nuclear RNA processing steps linked to canonical nuclear export. I. RNA polymerase II initiates the transcription of genomic DNA (red and blue helix) and produces a capped transcript (purple). The cap is recognized by the cap-binding complex (CBC). The TREX core complex THO and the adapters ALY (Ally of AML-1 and LEF-1) and UAP56 assemble at the CBC. II. The spliceosome assembles at the splicing sites of nascent mRNA and promotes the intron excision. The exon junction complex (EJC) is deposited 23 nt upstream of the splicing site where the Serine-Arginine-rich (SR) proteins remain attached to the mRNA. TREX1 interacts with the EJC and SR proteins. III. The cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor complex (CPSF) cleaves the nascent mRNA at the termination sites and promotes the synthesis of the poly(A) tail. IV. Nuclear RNA export factor 1 (NXF1)–NTF2-related export protein 1 (NXT1) exportins are recruited by the TREX1 complex starting at the 3′ end of the mature mRNP. V. NXF1–NXT1 interacts with TREX2 to direct the mature mRNP towards the nuclear pore complex (NPC) where the mRNP is exported through the interaction of NXF1–NXT1 with FG-Nups inside the NPC pore VI. During export, many protein components of the mRNP are removed, while others dissociate from the mRNA in the cytoplasm and are recycled to the nucleus. The square in the bottom right corner shows a more detailed representation of the NPC.