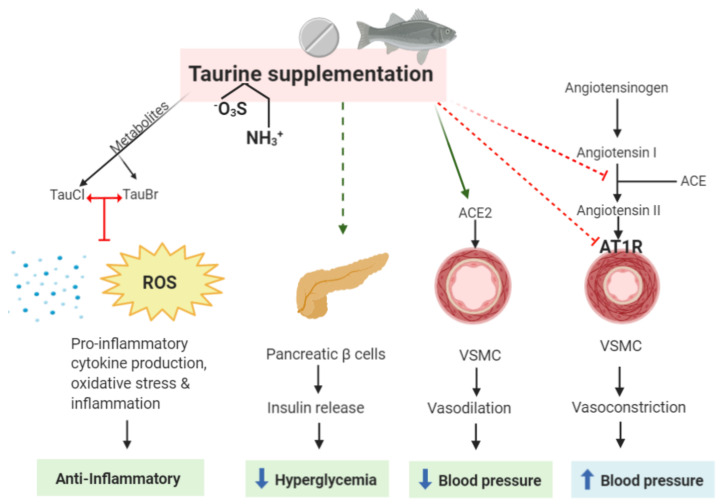
Figure 1.
Possible sites of action of taurine as a beneficial agent in treating cardiovascular disease (CVD) and its anti-inflammatory properties. The taurine metabolites, TauCl and TauBr, exert anti-inflammatory properties by blocking the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress (ROS), and inflammation. Taurine itself may directly reduce hyperglycemia, activate the protective arm of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) by increasing ACE2 expression, and inhibit the harmful axis of the RAS by reducing Ang II production, which is currently one of the main targets in treating CVD and coronary heart disease (CAD). It must be emphasized that taurine supplementation eliciting insulin release may be detrimental/have no effect in patients who are obese and have already elevated insulin levels. TauCl, taurine-chloramine; TauBr, taurine-bromamine; ROS, reactive oxygen species; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell; ACE, angio-converting enzyme; AT1R, AngII type 1 receptor.