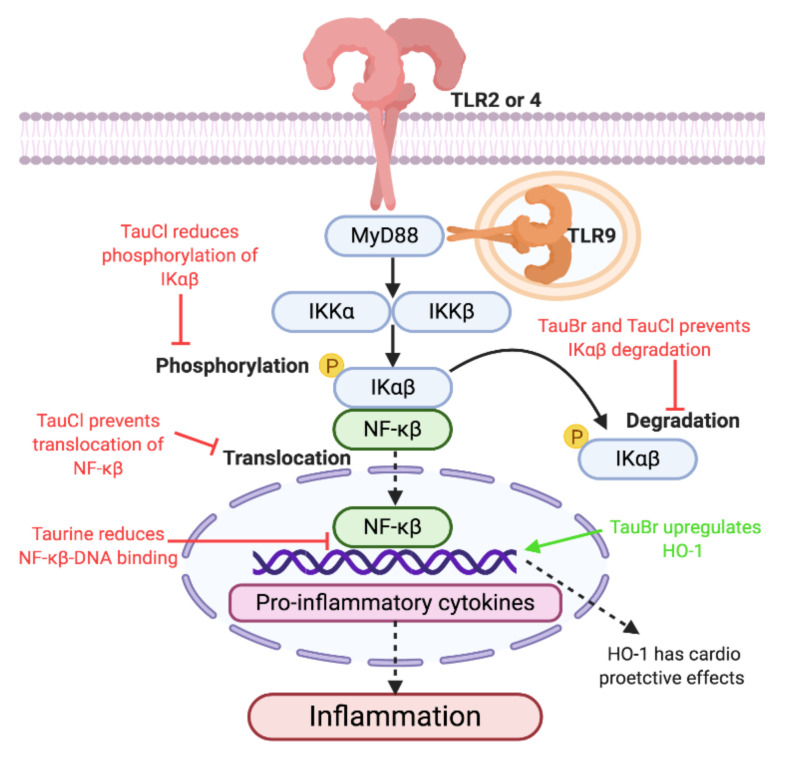
Figure 2.
Proposed anti-inflammatory mechanisms of taurine, taurine-bromamine, and taurine-chloramine via TLR/MyD88/NF-K (Toll like receptors/Myeloid differentiation primary response 88/Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated β cells) signal transduction. Due to the ability of taurine and its metabolites to reduce inflammation through TLR/MyD88/NF-K signal transduction, using them as therapeutics could result in decreased production of inflammation. Decreasing inflammation could improve cardiovascular disease (CVD) pathologies, as chronic inflammation caused by TLR activation has been implemented in disease pathogenesis and development. Therefore, the anti-inflammatory effect and increased release of heme oxigenase 1 (HO-1) may be therapeutic in CVD pathologies.