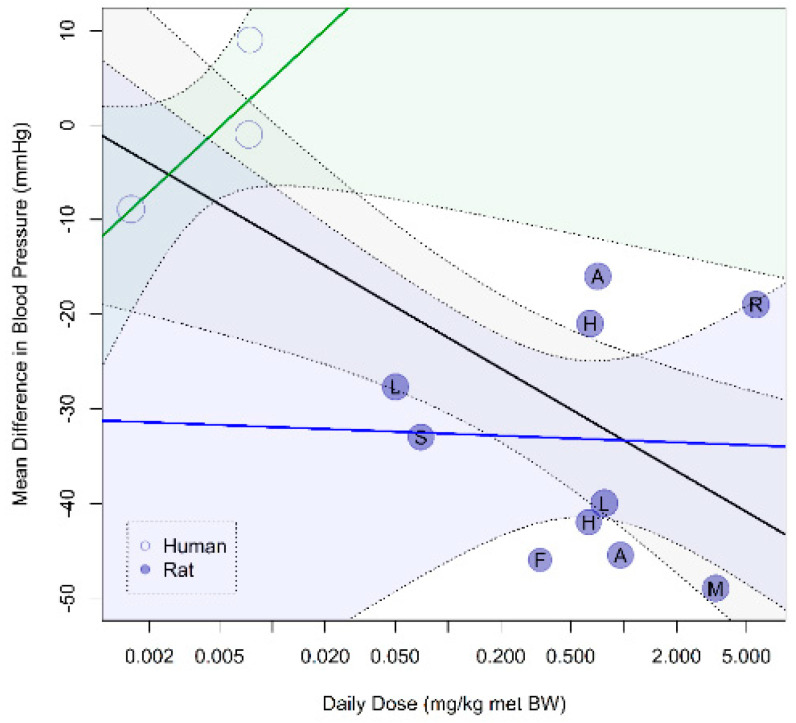
Figure A6.
Dose–response curve of prenatal supplementation of arginine family on blood pressure (BP) in complicated pregnancies: Higher doses of arginine result in lower maternal blood pressure in complicated pregnancies (pslope = 0.0031). However, this dose–response relation is influenced by an interspecies difference as the higher doses are tested in animal studies and the lowest doses are tested in human studies. Animal models for pregnancy complication included adriamycin nephropathy-induced preeclampsia (A), spontaneous hypertension and heart failure (F), hyperinsulinemic-induced PIH/FGR (H), L-NAME-induced fetal growth restriction/preeclampsia (L), magnesium deficiency-induced fetal growth restriction (M), reduced uterine perfusion pressure-induced fetal growth restriction/preeclampsia (R), and sonic stress-induced preeclampsia (S). Daily dose is expressed as mg per kg metabolic body weight. Open dots indicate human studies, and closed dots indicate animal studies. The black line is drawn for all studies, the yellow line is for animal studies only, and no line is drawn for human studies since only 3 studies were available.