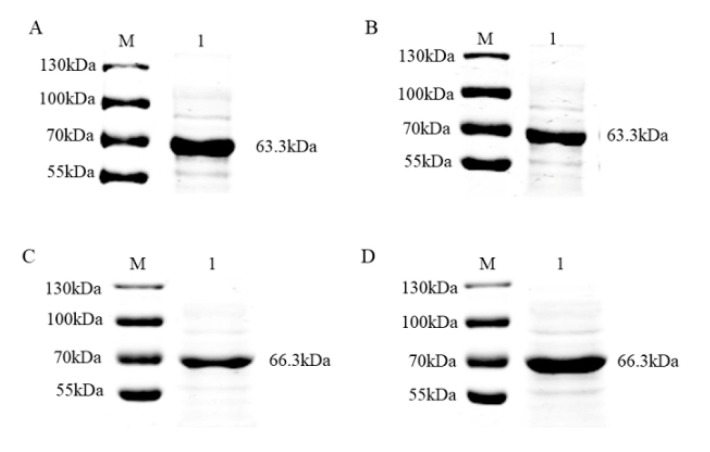
Figure 2.
Identification of PRV gE and gB proteins from the pMAL-c5x plasmid via immunoblotting. (A) Detection of PRV gE by His tagging. M, molecular weight marker; lane 1, supernatant of E. coli pMAL-c5x PRV gE after induction by IPTG and ultrasonic disruption. (B) Detection of PRV gE by MBP (Maltose binding protein) tagging. M, molecular weight marker; lane 1, supernatant of E. coli pMAL-c5x PRV gE after induction by IPTG and ultrasonic disruption. (C) Detection of PRV gB by His tagging. M, molecular weight marker; lane 1, supernatant of E. coli pMAL-c5x PRV gB after induction by IPTG and ultrasonic disruption. (D) Detection of PRV gB by MBP tagging. M, molecular weight marker; lane 1, supernatant of E. coli pMAL-c5x PRV gB after induction by IPTG and ultrasonic disruption.