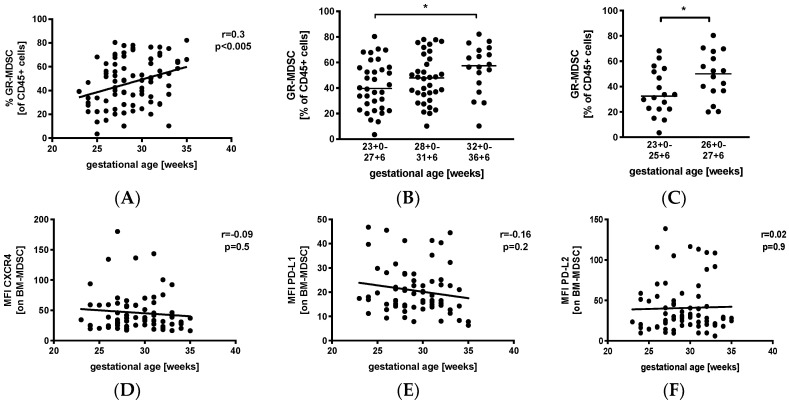
Figure 1.
Quantification of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (GR-MDSC) in the breast milk of preterm infants (dependency on gestational age). Milk cells were isolated from the breast milk of mothers of preterm infants during the first five weeks of life. Percentages of GR-MDSC (of total CD45+ leucocytes) and the expression of activation markers CXC-motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1), and programmed death ligand-2 (PD-L2) on breast milk containing a large population of GR-MDSC (BM-MDSC) were determined by flow cytometry. The mean percentages of BM-MDSC and the mean mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of activation markers over the first five weeks were calculated. (A) Scatter diagram showing the percentage of GR-MDSC of total milk leucocytes depending on gestational age. Regression line shows the correlation between percentages of BM-MDSC and gestational age. n = 86, Spearman correlation. (B) Scatter diagram showing the percentage of GR-MDSC of milk leucocytes from mothers of preterm infants delivered at <28 0/7 WOG, between 28 0/7 and 31 6/7 WOG and >32 0/7 WOG. n = 18–34, * p < 0.05; Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison test. (C) Scatter diagram showing the percentage of BM-MDSC from mothers of preterm infants delivered at <26 0/7 WOG, between 26 0/7 and 27 6/7 WOG, * p < 0.05; Mann–Whitney test. (D–F) Scatter diagrams showing the expression of CXCR4 (D), PD-L1 (E) and PD-L2 (F) on BM-MDSC depending on gestational age. Regression line shows the correlation between percentages of BM-MDSC and postnatal age. n = 86, p > 0.05, Spearman correlation.