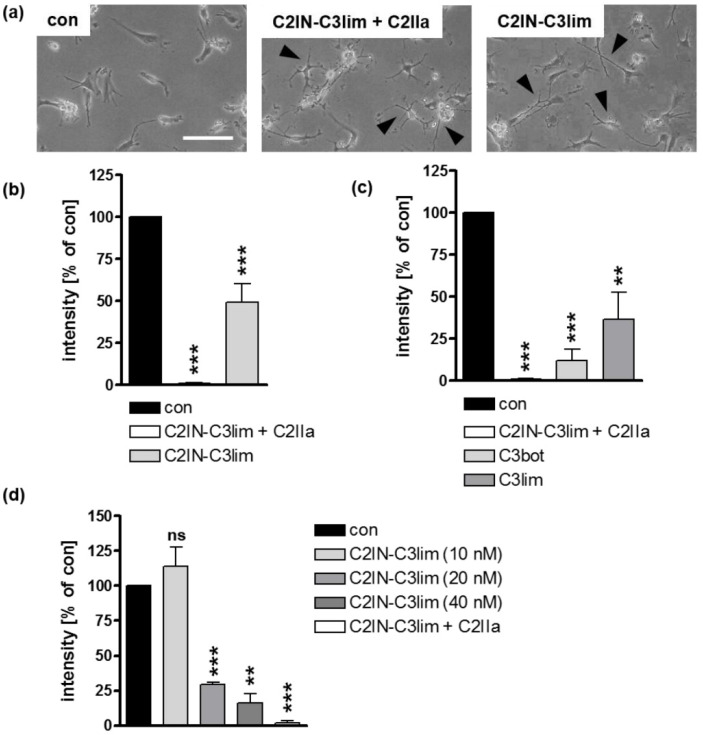
Figure 4.
C3 toxins are internalized into the cytosol of mature human monocyte derived DCs. (a) Mature human DCs were treated at 37 °C with C2IN-C3lim/C2IIa (5/8.5 nM), C2IN-C3lim (80 nM), or were left untreated (con). Representative phase contrast images after 3.5 h are shown. Scale bar correspond to 50 µm and holds for all images. Cells displaying obvious C3-morphology are marked with black arrow heads. (b) Subsequently, cells were washed, lysed, and incubated with freshly added C3 (300 ng) and biotin-NAD+ (10 µM) for 30 min at 37 °C. Afterwards, cell lysates were transferred to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis to detect biotin-labeled, i.e., ADP-ribosylated Rho proteins via peroxidase-coupled streptavidin. Equal protein loading was confirmed via Ponceau S staining of the membrane. Densitometrical analyses from several experiments (normalized to Ponceau S loading control) are given as mean ± SD (n = 4). (c) Mature DCs were treated at 37 °C with C2IN-C3lim/C2IIa (5/8.5 nM), C3bot (160 nM), C3lim (160 nM), or were left untreated (con). After 3.5 h, detection and densitometric quantification of ADP-ribosylated Rho was performed as described above (n = 4) (d) Mature DCs were treated at 37 °C with decreasing concentrations of C2IN-C3lim ranging from 40 nM over 20 nM to 10 nM. As a control, cells were treated either with C2IN-C3lim/C2IIa (10/17 nM) (positive control) or were left untreated (con). After 3 h, detection and densitometric quantification of ADP-ribosylated Rho was performed as described above (n = 2) (b–d) Significance was tested using a Student’s t test (ns = not significant, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).