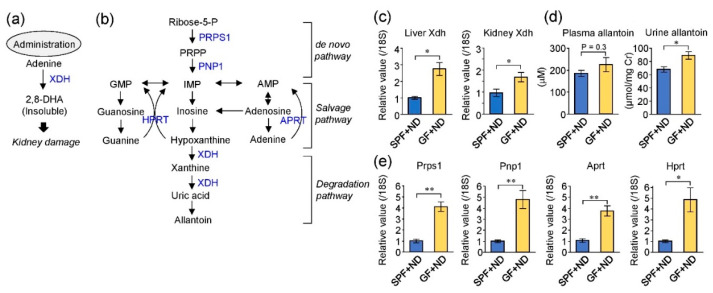
Figure 1.
Germ-free (GF) conditions increased the expression of purine metabolizing enzymes. (a) Pathway of kidney damage by the administration of adenine. 2,8-DHA, 2,8-dihydroxyadenine; XDH, xanthine dehydrogenase. (b) Metabolic pathway of purines. PRPS1, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1; PNP1, purine nucleoside phosphorylase 1; APRT1, adenine phosphoribosyl transferase; HPRT1, hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase. (c) Expression of XDH mRNA in the liver and kidney. Specific-pathogen-free (SPF) + ND, SPF mice with normal diet; GF + ND, germ-free mice with normal diet. (d) Plasma and urine allantoin levels. Urinary concentrations were corrected for urinary creatinine (μmol/mg urinary creatinine). (e) mRNA levels of genes corresponding to purine metabolizing enzymes in the liver. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared between indicated groups (t-test). n = 4 in SPF + ND and GF + ND groups.