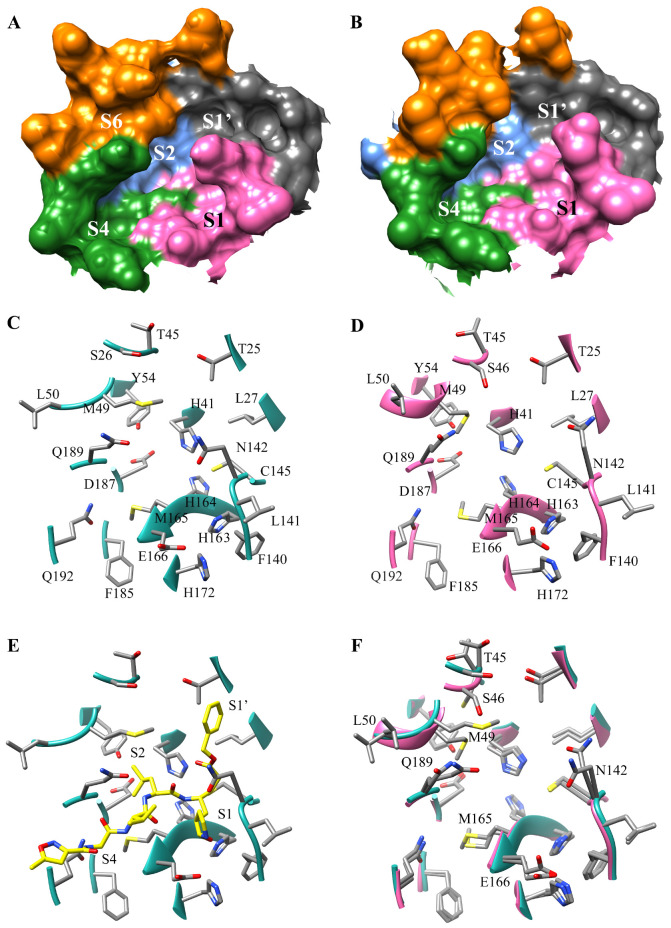
Figure 1.
Overview of SARS-CoV-2 Active site using PDB 6LU7 and 5R7Z: (A) Surface of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro active site in PDB 6LU7, regions colored represent the binding subsites S1, S1′, S2, S4, and the cleft S6, which is accessible in the 6LU7 receptor; (B) Surface of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro active site in PDB 5R7Z, regions colored represent the binding subsites S1, S1′, S2, S4. (C) Residues comprise the key active site regions in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro (PDB 6LU7); (D) Residues which make of the key active site regions in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro (PDB 5R7Z); (E) The ribbon structure of the 6LU7 crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro showing residues contributing to the S1, S2, S4 subsites. The N3 inhibitor is shown to assist in visualizing the subsite binding pockets. (F) Overlay of the 6LU7 (cyan) and the 5R7Z (pink) active sites. The highlighted residues are the residues shown to have different side-chain orientations.