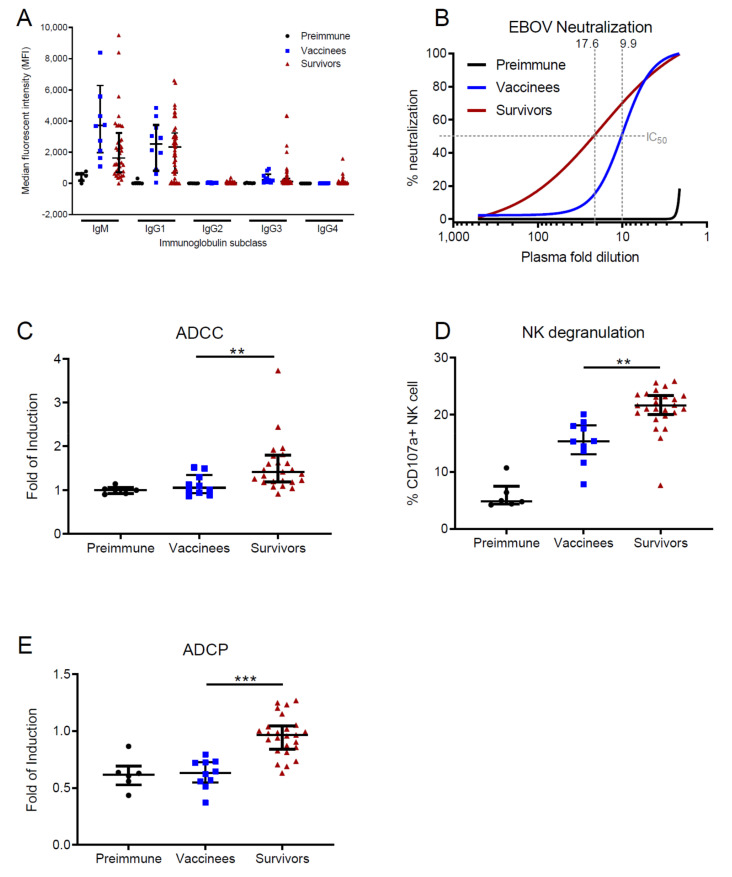
Figure 1.
Antibody quantity and functions in recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus vectored vaccine (rVSV-ZEBOV) vaccinees and Ebola virus disease (EVD) survivors. Plasma samples of individuals vaccinated with 2 × 107 PFUs of candidate vaccine rVSV ZEBOV 180 days after vaccination (vaccinees, n = 10, blue squares) were compared with plasma from EVD survivors (survivors, n = 25, red triangles). Median Ig levels of vaccinees before vaccination (preimmune, n = 6, black points) served as a control. Points show the individual measurements. Bars show the median as well as first and third quartile of the sample distribution. (A) Beads based ELISA for analysis of immunoglobulin (Ig) isotypes and subclasses. Shown is the Median Fluorescent Intensity (MFI) of the secondary antibody in logarithmic scale. (B) Plaque reduction (neutralization) assay using authentic EBOV (Mayinga variant). Lines indicate the nonlinear regression. IC50 values are indicated by light grey pointed lines. (C) Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) reporter assay. (D) Natural killer (NK) cell degranulation assay. (E) Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) reporter assay. In all graphs, significance is indicated in lines. Significance levels are calculated using Mann–Whitney tests and indicated by asterisks, namely ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001. IC50: half maximal inhibitory concentration.